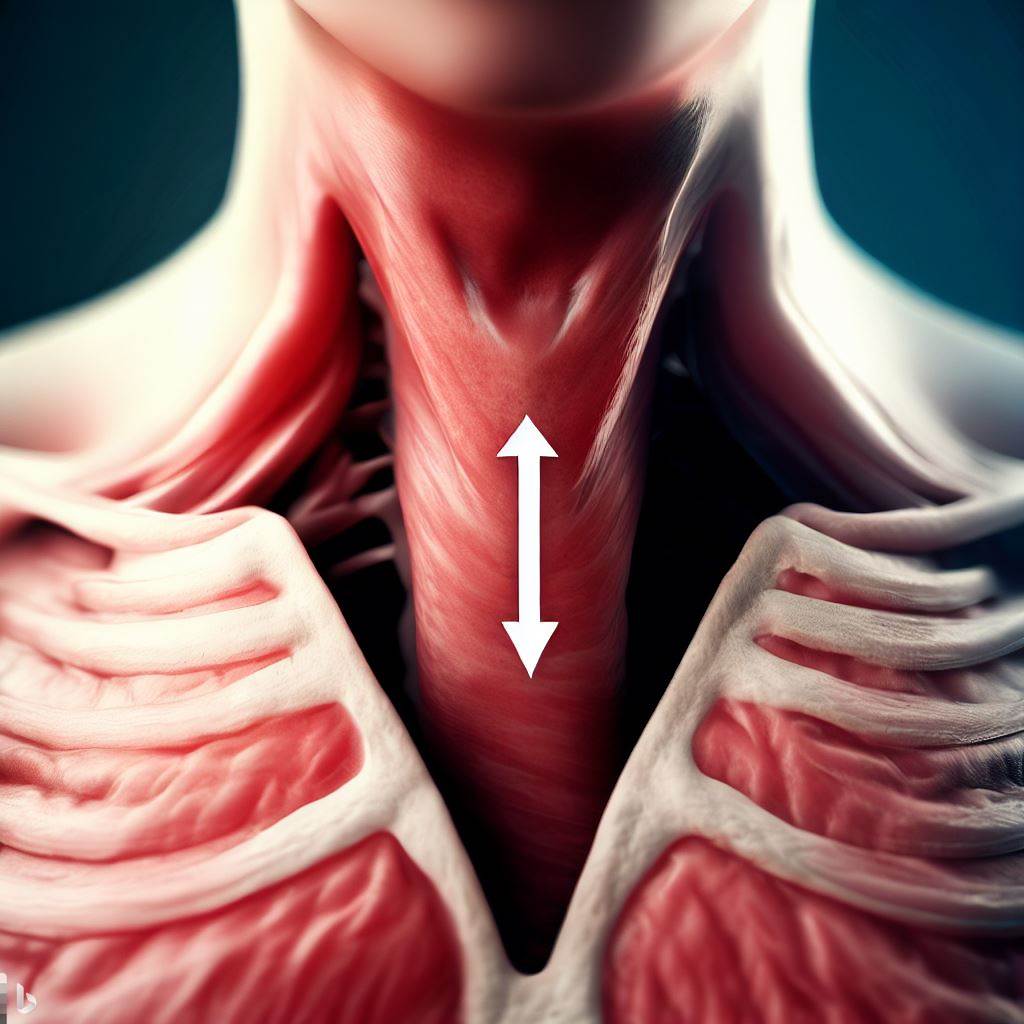
The suprasternal notch, also known as the jugular notch or jugular notch of the manubrium, is an anatomical feature located at the superior part of the sternum (breastbone), in the midline of the chest. It is a shallow concave depression or notch that can be felt or seen as a slight dip in the skin between the clavicles (collarbones).
The suprasternal notch serves as a landmark for various medical procedures and assessments. It is often used as a reference point for measuring the level of the jugular venous pressure (JVP), which provides important information about the function of the heart and fluid status in the body. In addition, it can be palpated during the examination of the neck and upper thorax, helping to identify anatomical structures and assess lymph nodes or masses.
Thus, the suprasternal notch is a useful anatomical landmark for healthcare professionals to locate and evaluate structures in the neck and upper chest region.
Suprasternal Notch Location
The suprasternal notch, also known as the jugular notch or jugular notch of the manubrium, is a shallow concave depression located at the superior part of the sternum, specifically on the manubrium. The sternum is a flat bone in the center of the chest, often referred to as the breastbone.
To locate the suprasternal notch, follow these steps:
- Stand or sit in an upright position with your head and neck in a neutral position.
- Place your fingers at the base of your neck, where the neck meets the upper chest.
- Gently slide your fingers downward along the midline until you reach the area just above the sternum.
- You will feel a slight dip or depression in the skin. This is the suprasternal notch.
The suprasternal notch is positioned between the medial ends of the clavicles (collarbones) and lies in the midline of the chest. It serves as a prominent landmark in the anatomical structure of the chest and neck region.
Once you have located the suprasternal notch, you can use it as a reference point for various medical procedures and assessments, as mentioned earlier. It can help in measuring the jugular venous pressure, examining the neck, or identifying structures during surgical procedures.
Please note that the depth and width of the suprasternal notch can vary among individuals, but it is generally easily palpable or visible as a shallow concavity in the skin.
Anatomy of Suprasternal Notch
The suprasternal notch, also known as the jugular notch or jugular notch of the manubrium, is an anatomical feature located at the superior part of the sternum, specifically on the manubrium. It is a shallow concave depression or groove in the bone.
- Sternum: The sternum, or breastbone, is a flat bone located in the center of the chest. It consists of three main parts: the manubrium, the body, and the xiphoid process. The suprasternal notch is found on the superior border of the manubrium.
- Manubrium: The manubrium is the superior portion of the sternum. It is a triangular-shaped bone that articulates with the clavicles (collarbones) laterally and the body of the sternum inferiorly. The suprasternal notch is formed by the articulation of the medial ends of the clavicles with the superior border of the manubrium.
- Articulation: The suprasternal notch is created by the junction or articulation of the medial ends of the clavicles with the superior border of the manubrium. This articulation forms a small depression or groove that is easily palpable or visible on the surface of the chest.
- Ligaments: The suprasternal notch is reinforced by several ligaments that help stabilize the clavicles and the sternum. The ligaments involved include the interclavicular ligament, which spans between the medial ends of the clavicles, and the sternoclavicular ligaments, which connect the clavicles to the sternum.
- Variations: The depth and width of the suprasternal notch can vary among individuals. In some cases, it may be more pronounced and easily visible, while in others, it may be less noticeable. The size and shape of the notch can also be influenced by factors such as age, gender, and individual anatomical variations.
The suprasternal notch serves as an important anatomical landmark for healthcare professionals during various medical procedures and assessments. It can be used as a reference point for measuring the jugular venous pressure, examining the neck, or guiding surgical interventions in the chest and neck region.
Palpation of Suprasternal Notch
Palpation is a physical examination technique that involves using the sense of touch to assess various structures and characteristics of the human body. It is a method by which healthcare professionals, such as physicians, nurses, or physical therapists, gather information about the patient’s condition.
During palpation, the healthcare professional applies gentle pressure with their hands or fingers to different parts of the body, such as the skin, muscles, bones, organs, or other tissues. By palpating, they can assess various factors, including texture, temperature, moisture, tenderness, swelling, masses, and the presence of abnormalities.
You can palpate the suprasternal notch by placing your fingers just above the upper part of the sternum, between the clavicles. It is generally easy to locate as a slight dip or depression in the skin.
Here’s how to palpate the suprasternal notch:
- Positioning: The person being examined should be in an upright position, either sitting or standing. Make sure their head and neck are in a neutral position, not tilted or excessively flexed or extended.
- Locate the Clavicles: Begin by identifying the medial ends of the clavicles, also known as the sternal ends. These are the portions of the clavicles that attach to the sternum. The clavicles are prominent bones that run horizontally across the upper chest, just above the suprasternal notch.
- Identify the Suprasternal Notch: Place the pads of your fingers (usually the index and middle fingers) at the base of the person’s neck, where the neck meets the upper chest. Gently slide your fingers downward along the midline of the chest, following the path between the clavicles.
- Feel for the Depression: As you slide your fingers downward, you will come across a slight dip or depression in the skin. This is the suprasternal notch. It may feel like a shallow groove or concavity in the bone.
- Assess the Notch: Once you have located the suprasternal notch, take note of its characteristics. It may vary in depth and width among individuals. Pay attention to any tenderness, abnormal bumps, or other findings that could indicate pathology.
- Document and Communicate Findings: If you are performing a clinical examination, make sure to document your findings accurately in the medical record. Note the depth, width, and any notable features of the suprasternal notch. Communicate any abnormal findings to the appropriate healthcare professional.
Clinical significance of Suprasternal Notch
The suprasternal notch is an important landmark used in various clinical assessments:
- Jugular Venous Pressure (JVP): The suprasternal notch is used as a reference point for measuring the level of the JVP. By observing the height of the jugular venous pulsation relative to the suprasternal notch, healthcare professionals can assess the pressure in the right atrium and the venous system. This information is helpful in diagnosing and monitoring conditions such as heart failure.
- Examination of the Neck: The suprasternal notch can be palpated during the examination of the neck and upper thorax. It serves as a reference point for locating anatomical structures, such as the thyroid gland and the trachea. It also aids in assessing lymph nodes or detecting any masses or abnormalities in the region.
- Surgical Procedures: The suprasternal notch can be used as a landmark during certain surgical procedures involving the neck and upper chest. Surgeons may use it as a reference point for making incisions or accessing deeper structures.
- Central Venous Catheter Placement: The suprasternal notch can also be used as a guide for the placement of central venous catheters. It helps to locate the appropriate entry point for the catheter, facilitating the safe and accurate placement of the catheter into the central venous system.
- Radiological Imaging: In radiological imaging, the suprasternal notch can be used as a reference point for measuring anatomical structures and evaluating pathology in the chest and neck regions. It aids in determining the position and orientation of various structures seen on imaging studies, such as X-rays, CT scans, or MRI scans.
It’s important to note that the clinical significance of the suprasternal notch may vary depending on the specific context and medical procedure being performed. Healthcare professionals utilize the suprasternal notch as an important anatomical landmark for assessment, diagnosis, and treatment planning in various clinical scenarios.