Contained Spinal Disorder or bulging disc is an anomalous condition which occurs along the spine, in the lower back or lumbar region. In rare cases, bulging disc can also affect the neck area. The disorder is caused due to the natural process of intervertebral discs degeneration, and hence commonly observed in older people.
It may be noted that the spinal cord in humans is surrounded by the spine, which in turn is made of several intervertebral discs. The primary function of the spinal system is to offer support for the body weight. However, due to increased stress as well as the onset of old age, degeneration of the discs can occur. The affected discs lose their spongy nature and flexibility, and are thus unable to carry out their function of resisting impact and absorbing shocks to the body.
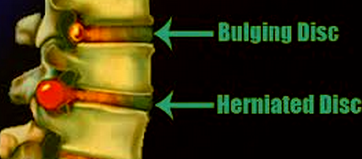
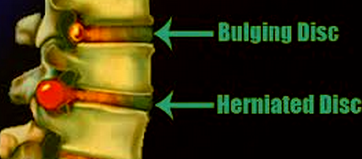
Characteristics of bulging disc
- Bulging disc is a medical term used to describe an abnormal condition of the spine.
- The disorder usually affects the lower back or the lumbar area.
- Bulging disc is a sign of a disc which has moved or shifted from the main radius.
- It is usually a part of the ageing process.
- One of the prominent features of bulging disc is the presence of a lump or a bulge in one or several discs of the spine. The bulge can be observed through an opening and is majorly comprised of soft, gelatinous substance.
- Bulging disc rarely causes pain. However, patients who experience discomfort will elicit back pain which radiates to the legs.
- Even though bulging disc generally affects the lower back or lumbar region, it may also occur in the neck region. This form of bulging disc is characterized by sharp pain between the arms and shoulders. The pain may also signify presence of a pinched nerve in the area.
Difference between a bulging disc and herniated disc
A bulging disc is quite different from another spinal condition referred to as herniated disc. Bulging disc generally tends to occur slowly over a period of time, while herniated disc has a sudden onset.
Herniated disc is caused due to an injury or a trauma to the spinal region, or to the areas surrounding it. On the other hand, bulging disc usually develops as part of the bone degeneration which accompanies the natural process of aging. Bulging disc also does not involve pain, unless it obstructs a nerve or experiences trauma.
The risks associated with bulging disc
Individuals who experience any of the symptoms of a bulging disc should consult a doctor. Also, patients should never ignore discomfort or pain of the lower back, legs, hips, neck, or arms, especially if such pain is chronic.
Untreated cases of bulging disc can result in a lot of complications. It can progress to become herniated disc. In rare cases, the bulge may burst as well. This will not only aggravate the condition, but also result in abnormal posture and restrictive motion.
Treatment of bulging disc
Bulging disc usually does not cause any visible symptoms such as acute back pain, etc. Hence, the condition is generally diagnosed during a routine examination or when seeking treatment for some other health problems. It is usually detected via an MRI of the lower back region.
As discussed above, bulging disc generally does not cause any problems unless it ruptures or herniates. Treatment for bulging disc typically involves limiting physical activities like lifting weights, plenty of back rest, etc. Other remedial measures include the following:
- A mixture of heat and ice therapy
- Use of Pain killer drugs to alleviate pain
- Cortisone injections.
- Anti-inflammatory medicines
- Physiotherapy which involves special exercises for the back
- Surgery is recommended to correct only extreme cases of bulging disc
Exercises for bulging disc
There are several exercises that patients can do to alleviate bulging disc pain. The main aim of these exercises is to enhance the blood flow to the nerves spinal discs, muscles, and ligaments affected by bulging disc. The improved blood circulation will supply essential nutrients to the bulged disc and thus aid the healing process. It will also numb the pain of pinched nerves. It is important to do warm-up exercises to reduce stiffness and thus decrease chances of muscle injuries. Additionally, the below listed exercises will strengthen the muscles, thereby correcting the body posture. A few exercises are listed below:
- Use a large ball, sit on it, and roll your buttocks up and down for about five minutes. It will ease back pain
- Use a mini trampoline and march on it. Do not jump as it will aggravate the condition. This exercise will help strengthen the muscles
- A pelvic tilt is a stretching exercise and great for bulging disc patients. Patients need to lie on their backs with folded knees and gently lift up the legs, with the back touching the floor. Remain in the position for about 5 seconds.
- Semi sit-ups, knee rolls, back extensions, and knee chest are some of the other useful stretching exercise.