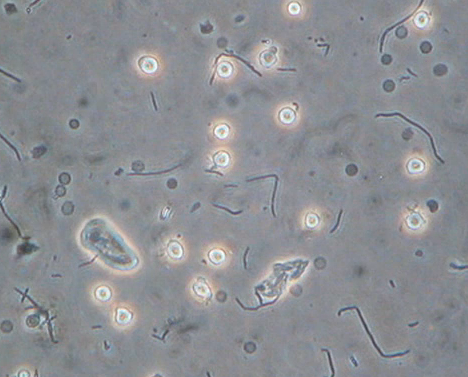
White blood cells are present in the immune system to fight off infectious foreign particles entering the body. In abbreviated form, it is referred to as WBCs.
The quantity of WBCs in blood helps to know the health condition of a person. These cells usually are not found in urine as urine has no blood cells and is basically sterile. However, if WBCs are detected in urine it means something is wrong with the immune and urinary system. Also, a white blood cell in urine indicates a possibility of underlying diseases; this could be due to inflammation or infection of the urinary tract or the kidneys.
Presence of white blood cells in urine is known as ‘Hematuria’. Normally, the kidney filters the blood and prevents white blood cells from entering into urine. But due to infection the kidneys stop its normal way of functioning, thereby allowing white blood cells to pass into urine. Infection can also flow from the urinary tract to the kidneys.
The major causes of white blood cells in urine are infection in bladder and kidneys, with the most common cause being infection of the urinary tract. Some of the symptoms are frequent urination, burning sensation, painful urination, fever, and pain in abdomen. Some of the infections can be treated through medications whereas serious cases may be treated through surgical methods.
Symptoms
Some of the symptoms that may accompany a case of white blood cells in urine are as follows:
- Painful urination
- Burning sensation
- Frequent urination
- The color of the urine may look cloudy
- Strong smelling urine
- Fever, chills
- Blood in the urine
- Abdominal pain
- Weakness
- Disturbances in sexual intercourse, bladder clearance, and conditions related to pregnancy.
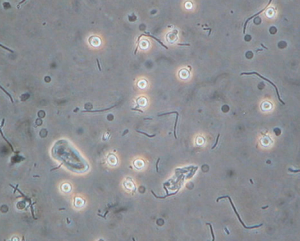
Causes of white blood cells in urine
Three major causes of white blood cells in urine are as follows:
- Infection in Urinary tract: Urinary tract infection is a common type of infection that affects the urinary system. When germs enter the urethra, it may result in WBCs in urine. This may happen during voiding or sexual intercourse. This further leads to burning sensation and painful urination.
- Infection in Bladder: One of the important parts of the urinary system is the bladder. Therefore, any abnormality in the bladder due to infectious bacteria can lead to collection of WBCs in urine. This may further cause painful and burning sensations while urinating. The urine may also get a cloudy appearance.
- Infection in the kidneys: Normally, the function of kidney is to filter the blood and prevent white blood cells from entering urine. A common cause for white blood cells in urine is kidney infection. Infection in kidney is also known as ‘Pyelopnephritis’. In this case when white blood cells are found in urine it indicates bacterial infection. Infection can begin from the urinary tract and slowly spread from the urinary tract to the kidneys. This further leads to abnormal functioning of the kidneys, thereby allowing white blood cells to enter the urine. Mostly, women are affected with this type of infection in comparison to men.
- Other causes:There are few other reasons such as obstruction or disturbances in the urinary system due to kidney or bladder stone, tumor, interstitial cystitis etc. which can cause white blood cells in urine.
- Interference during sexual intercourse or abnormal bladder clearance.
- Some conditions connected to pregnancy can also cause white blood cells to be collected in urine.
Treatment of white blood cells in urine
The best way to prevent and treat white blood cells in urine is to avoid occurrence of infection in urinary tract as much as possible. Still if infection occurs, basically there are two methods to cure it, namely:
- Antibiotics: To treat cystitis, pyelonephritis antibiotics can be used.
- Surgical methods:Obstructions in the urinary system could be due to tumor, kidney stone etc. causing white blood cells in urine. At times it may be treated with the help of medicines but in serious cases it requires surgical treatments.
- Kidney stones can be removed surgically or ultrasonically.
- In case of interstitial cystitis, antibiotics are not much effective. In some cases it can be treated by instilling medicines or widening the bladder.
In short, it can be said that most cases of white blood cells in urine are caused due to urinary tract infection. Also in few cases, if the infection is external, then it can cause inflammation of genitals. High proportion of white blood cells is a signal of bacterial infection and in some cases it indicates serious health problems. This could be systemic lupus erythematosus or tumor in bladder which in turn affects the entire body. The best treatment that can be opted to cure is to keep away from infections as much as possible. Still, if infection occurs it can be treated with antibiotics which will do away with the WBCs in urine. Sometimes disease can be very serious and may require surgical treatment, this is determined on the basis of the frequency and severity of the infection.