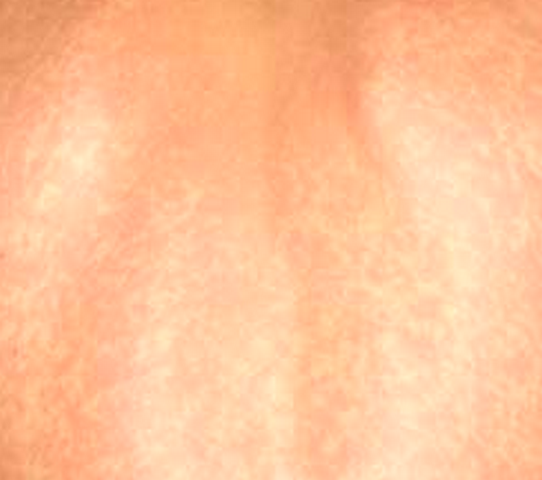
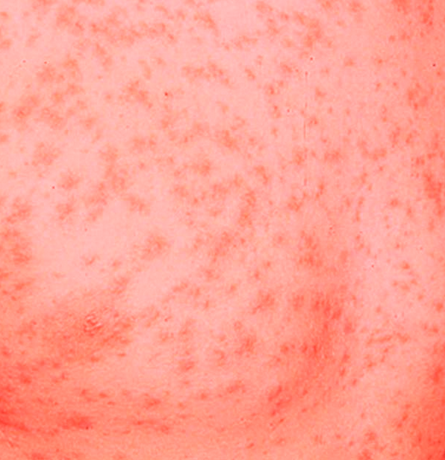
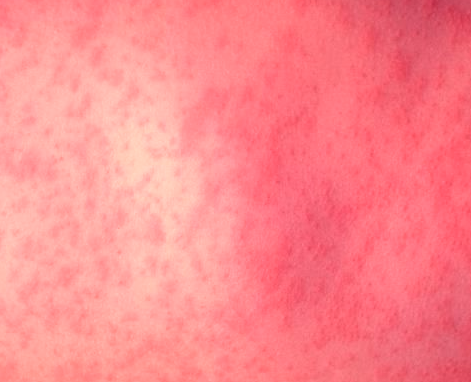
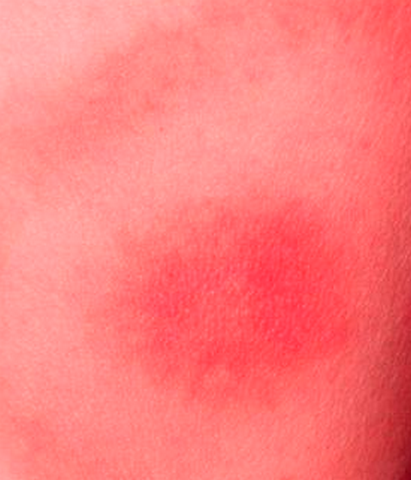
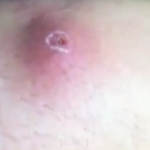
West Nile virus rash is caused due to a viral infection transmitted by mosquitoes. Most individuals affected by this type of rash do not elicit any symptoms; or they may elicit only mild signs like minor headache and fever. However, some affected individuals may experience a deadly illness that also involves brain inflammation.
Minor symptoms of West Nile virus typically disappear without any treatment. However, the serious symptoms of the disease, including intense headache, confusion, fever, or unexpected weakness need to be checked by a doctor.
The risk to developing West Nile virus rash increases with exposure to mosquitoes occurring in areas where the West Nile virus is prevalent. People can decrease the risk by wearing adequate clothing and using mosquito repellants to protect themselves from mosquito bites.
Symptoms of West Nile virus rash
Most patients infected by the West Nile virus may not experience any signs or symptoms, including formation of West Nile virus rash.
Around 20 percent of patients may get affected by a minor infection known as West Nile fever. It can result in the following signs and symptoms:
- Headache
- Fever
- Body pain or aches
- Pain in the back
- Fatigue
- Occasionally, the West Nile virus rash may appear
- Eye pain in some cases
- In rare instances, the lymph glands may experience swelling
Infection by West Nile virus may cause a deadly neurological effect in less than one percent of patients. It can result in encephalitis or inflammation of the brain; meningitis, i.e. inflammation of the spinal cord and the meninges; meningoencephalitis, i.e. inflammation of the brain as well as the surrounding membranes; West Nile poliomyelitis or spinal cord inflammation; and acute flaccid paralysis which is characterized by sudden weakness in the legs, arms, or respiratory muscles. Some of common signs and symptoms of severe West Nile virus infection are listed below:
- Intense headache
- Pain
- Fever with high temperatures
- Neck stiffness
- Coma or stupor
- Confusion or disorientation
- Muscle twitching or jerks, or tremors
- Fits or convulsions
- Decreased or absent coordination
- Sudden weakness of the muscles or partial paralysis
The symptoms of West Nile virus fever along with the West Nile virus rash typically persist for some days. However, the signs of meningitis or encephalitis can last for many weeks and some neurological anomalies like muscle weakness may become permanent.
Causes of West Nile virus rash
West Nile virus rash is caused due to infection by the West Nile virus, which is generally transmitted to animals and humans via mosquito bites. Mosquitoes become carriers of the virus after feeding on infected birds. The infection cannot transfer through kissing or touching a patient.
A majority of West Nile virus rash infections happen during the active season for mosquitoes, i.e. in warm weather. The signs and symptoms of West Nile virus rash usually occur around 3 to 14 days after getting bitten by an infected mosquito.
West Nile virus is found in some regions of Asia, Africa, and the Middle East. It made its first appearance in the United States in the summer of 1999. Currently, the disease occurs in all the 48 continental states.
It may also be noted that West Nile virus rash infections can also transmit via other routes such as blood transfusion and organ transplant. Hence, blood donors are screened for presence of the virus, which has substantially reduced the risk to its transmission through blood transfusions.
There exists some inconclusive evidence indicating the transmission of West Nile virus from a mother to a child during breastfeeding or pregnancy. It is however a very rare scenario.
The below listed risk factors can increase the vulnerability to developing West Nile virus rash:
- Even though West Nile virus rash infections occur throughout the United States, it is more prevalent in the Southern and Midwestern states.
- Most instances of West Nile virus rash infections occur between July and September.
- People who spend lots of time in the outdoors, for work or leisure, are at greater risk to getting bitten by a mosquito carrying theWest Nile virus.
- Individuals with a compromised immune system or those older than 50 years are at greater risk to developing the severe forms of West Nile virus rash infections.
Treatment of West Nile virus rash
A majority of individuals affected by West Nile virus rash infections recover without any treatment. The illness usually disappears on its own.
- Patients may take OTC pain killer medications for alleviating muscle aches and minor headaches.
- Children and teenagers should not be given aspirin as it is known to cause the deadly Reye’s syndrome in children recovering from flu-like conditions or chickenpox.
- Meningitis and encephalitis have no direct cure. Such patients may be give supportive care in a hospital with medicines and intravenous administration of fluids to prevent other kinds of health complications.
Controlling the growth of mosquitoes and following self-care guidelines to protect oneself from mosquito bites can help reduce the risk to developing West Nile virus rash.
West Nile Virus Rash Pictures