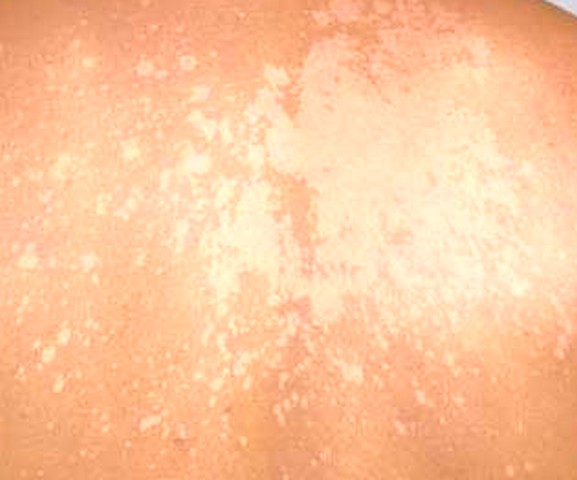
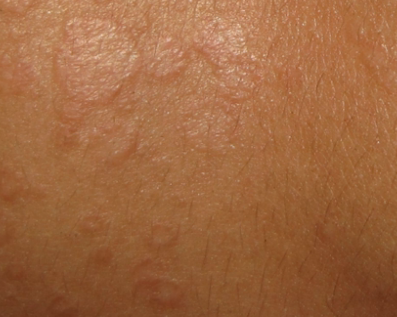
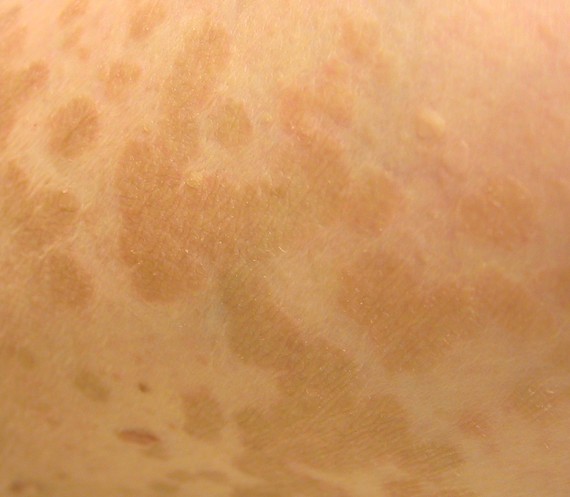
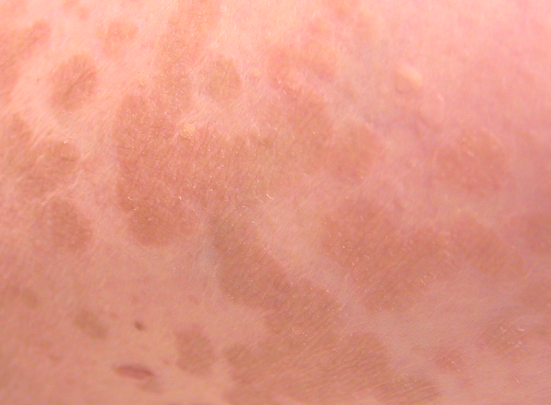
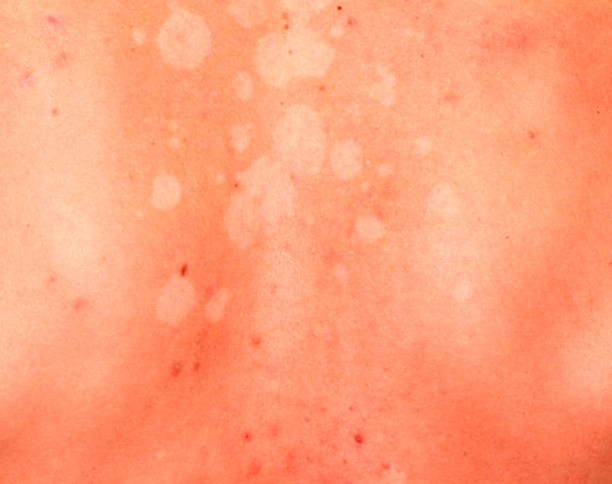
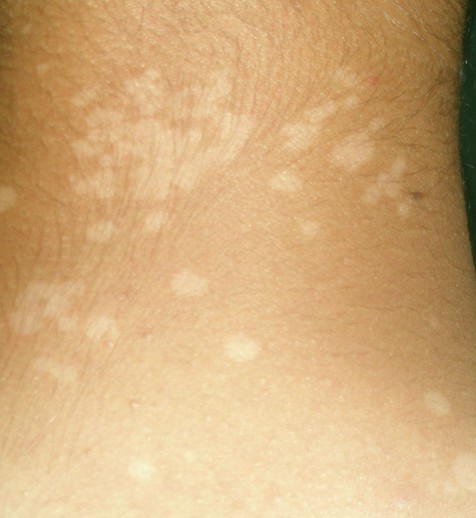
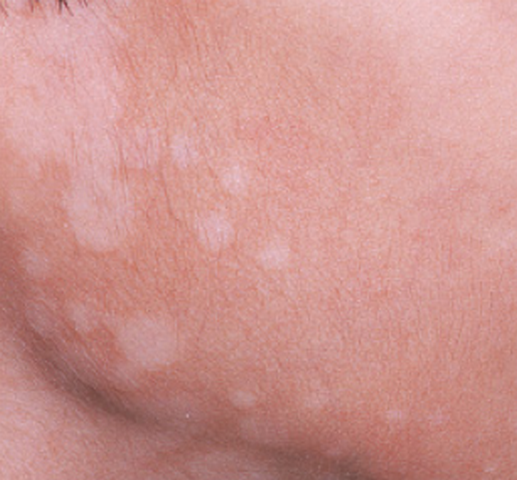
Tinea versicolor is a type of fungal skin infection caused by a yeast species that naturally occurs on the human skin. The skin disease, identified by an abnormal rash on skin, is caused due to uncontrolled growth of the yeast. Tinea versicolor is also known as pityriasis versicolor.
The fungus hampers normal skin pigmentation leading to formation of tiny discolored patches, which are darker or lighter than the nearby skin. Commonly affected areas include the shoulders and trunk, while young adults and teens are most prone to developing tinea versicolor. Exposure to sunlight may cause the abnormal patches to look more obvious.
Antifungal lotions, creams, or shampoos are used to eliminate tinea versicolor. It may however be noted that the abnormal skin color may persist for many weeks even post successful treatment. It is also possible for the skin condition to recur under amiable conditions of humid and warm weather.
Symptoms of tinea versicolor
Excessive growth of the yeast results in release of acidic bleach which in turn causes some sections of the skin to turn into a color that is different from the surrounding skin. Such abnormal skin patches may occur as one solitary discolored spot, or it may occur in clusters.
Some of the common signs and symptoms that accompany a tinea versicolor skin infection are listed below:
- Appearance of abnormal patches on skin which may be pinkish, whitish, brownish, or red. As compared to the adjacent skin, these patches may be of a darker or lighter shade.
- The anomalous spots can affect any part of the body, but are usually found on the chest, neck, arms, and back.
- The patches may not tan in the same manner as the rest of the skin.
- In some cases, the spots may cause discomfort or itchiness, or they may be scaly and dry.
- The patches tend to vanish during cool weather conditions, while they may deteriorate in humid and warm climates.
Causes of tinea versicolor
The fungus/yeast that causes tinea versicolor naturally grows on even healthy skin. The skin infection only begins due to overgrowth of the fungus. There are many factors which can activate an overgrowth of the fungus, such as:
- Residing in a tropical country with hot weather
- Presence of oily skin
- Presence of a compromised immune system
- Excessive perspiration
Tinea versicolor is not a contagious disease since the yeast is naturally found on human skin. It can occur in people with any skin color. Teens and young adults are however more susceptible to developing the skin infection.
Diagnosis
A visual examination of the abnormal skin patches is sufficient for a doctor to diagnose a case of tinea versicolor. Sometimes, the health care provider may use UV light to check the patches. UV light causes the affected skin regions to become florescent yellowish-green, in case they arise due to tinea versicolor.
The physician may also scrape-off some scales and skin from the affected region and microscopically examine the specimen. In children, the physician may attach a clear tape to the region and then remove it to lift the skin cells. It is then put onto a slide and investigated under a microscope.
Treatment of tinea versicolor
Tinea versicolor is treated with topical and oral medications. The type and scope of treatment is dependent on the location, size, and thickness of the region that is infected.
Common treatment options for tinea versicolor include:
- Topical anti-fungal medicines:The growth of yeast can be controlled by applying anti-fungal creams, lotions, soaps, shampoos, or foam on the affected spots. Doctors may suggest the use of OTC anti-fungal topical drugs that contain ingredients like pyrithione, zinc, selenium sulfide, clotrimazole, miconazole, and terbinafine, or prescription topical drugs in rare cases.
- Oral anti-fungal medications: Severe or recurrent instances of tinea versicolor are treated with anti-fungal pills. They may also be used to get quicker and simpler resolution from the skin infection. It may however be noted that anti-fungal pills have to be prescribed by a doctor, and may result in side effects.
Treatment generally helps resolve the fungal infection. However, the skin discoloration may persist for many months before returning to normalcy.
As the yeast normally occurs on skin, recurrent instances of tinea versicolor are quite common. You may use medicated cleansers 1 to 2 times a month to prevent the recurrence of the skin condition. Patients with recurrent episodes who live in humid and warm regions may need to regularly use such cleansers.
The below listed tips may be followed for effective management of tinea versicolor:
- Decrease the instances of sun exposure, as contact with sunlight can activate or aggravate an episode.
- Use non-greasy sunscreen with at least 30 SPF on a daily basis.
- Do not use oily skin products
- Reduce perspiration by using apparels made from light, breathable fabrics.
- Avoid wearing body-hugging or tight clothes.
Tinea versicolor pictures