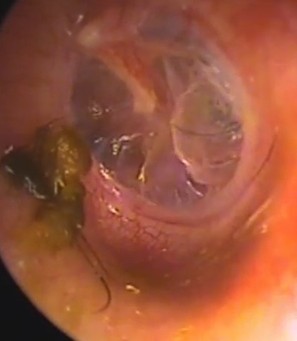
The eardrum is a flexible, very thin membrane which separates the middle ear from the outer ear. It is medically referred to as the tympanic membrane.
A retracted eardrum refers to a condition wherein the eardrum gets pulled or sucked into the area occurring behind it. This occurs when the pressure in the middle ear area becomes very low. A retracted eardrum is mostly caused due to infections. However, a rapid change in the external air pressure can also lead to a sudden drop in the pressure within an individual’s ear, and possibly cause a retracted eardrum.
Symptoms
- One of the most common symptoms of a retracted eardrum is elevated hearing sensitivity. Affected individuals usually hear most sounds to be somewhat louder than they actually are. The sensation may be similar to the feeling that we experience during air travel related pressure alterations.
- Patients may also suffer from ear pain.
Complications
Untreated cases of a retracted eardrum can result in development of retraction pockets in the middle ear. Debris may collect in such pockets and be at increased risk to infection, eventually resulting in a case of chronic infection. It can also lead to the development of a harmful condition called cholesteatoma. This serious complication of a retracted eardrum is characterized by trapping of a mass of skin in the middle ear space. Such a cyst can destroy the tympanic membrane. A big tumor-like growth may also cause erosion of the bones present in the middle ear, finally resulting in loss of hearing.
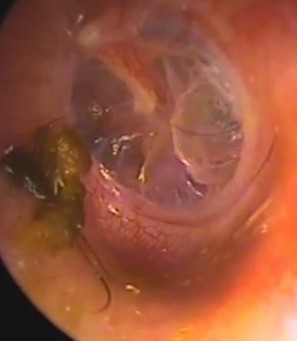
Causes of a retracted eardrum
- The eardrum is situated between the middle ear and the outer ear canal. In humans, the middle ear is connected to the throat and nose via a thin tube referred to as the Eustachian tube. This tube helps maintain correct pressure inside the middle ear with regards to the external pressure. The Eustachian tube also helps drain middle ear secretions, thereby preventing the onset of any ear infections.
- The air pressure on either side of the tympanic membrane is almost similar under normal conditions. However, any kind of blockage or dysfunction of the Eustachian tube can result in buildup of negative or low pressure inside the ear, leading to creation of a vacuum and ultimately a retracted eardrum.
- Allergies, inflammation of the sinuses, and upper respiratory tract infections are some of the common causes of a blocked Eustachian tube. Ear infection is considered as the main cause of such blockages.
- Whenever there is an ear infection, fluids tend to accumulate in the middle ear or the inner ear. Such fluid deposits can occasionally clog the Eustachian tube opening in the ear. This prevents the entry of outside air into the middle ear space, thereby causing increased negative pressure within the ear, eventually resulting in a retracted eardrum.
- The occurrence of masses or tumors in the naso-pharynx region can also result in Eustachian tube obstruction, which may then cause the eardrum to be sucked inwards, leading to a retracted eardrum.
- A retracted eardrum can affect children as well as adults. It is however more common in children, particularly in those who suffer from recurrent episodes of ear infections.
Diagnosis
Any type of ear infection, including a retracted eardrum, is diagnosed via examination of the patient’s ear with the help of a tool called an otoscope. This medical instrument can help verify whether an eardrum is retracted, bulging out, or inflamed.
Treatment of a retracted eardrum
Most instances of a retracted eardrum are not serious. The Eustachian tube tends to clear by itself and hence treatment is usually not required.However, as a retracted eardrum can progress to severe cholesteatoma it is advisable to contact a doctor for treatment. Medical treatment of a blocked Eustachian tube and a retracted eardrum also helps in finding relief from ear pain and other associated symptoms.
- Eustachian tube obstructions arising out of allergies, infections of the upper respiratory system, or sinusitis can be treated with home remedies and drug therapy. Antibiotic ear drops, painkillers, warm compresses, and nasal decongestants can be used to alleviate the symptoms and find relief.
- Doctors may also suggest use of the ‘valsalva maneuver’ for equalizing the pressure on either side of the ear. The maneuver involves holding the breath and tightening the body as if one was straining to have a bowel movement.
- Yawning, or opening and closing one’s mouth can help raise the pressure inside the ear, thereby equalizing it with external pressure.
- Severe instances of a retracted eardrum may require draining of liquids from the middle ear via use of a tympanostomy ear tube.
- Cholesteatoma or retraction pockets with infections can be eliminated via different kinds of surgical methods.
It is important for patients suffering from any kind of Eustachian tube blockage to consult a doctor for early treatment as it is typically the most common cause of ear infections and a retracted eardrum.