Water retention is a condition marked by abnormal buildup of fluid in tissues. It is medically referred to as edema. Any area of the body can get affected by water retention, but it is often more prominent in the arms, hands, ankles, feet, and legs.
Edema can occur due to varied causes, including pregnancy, intake of certain drugs, or presence of underlying conditions such as liver cirrhosis, kidney disorder, or heart failure.
Normal cases of water retention can be treated via reduced salt intake and medications for eliminating excess fluids. Water retention caused due to pre-existing diseases can be alleviated via treatment of those conditions.
Symptoms
Some of the common signs and symptoms of water retention are as follows:
- Shiny or stretched skin
- Puffiness or swelling of the tissue present just below the skin.
- Increase in the size of the abdomen
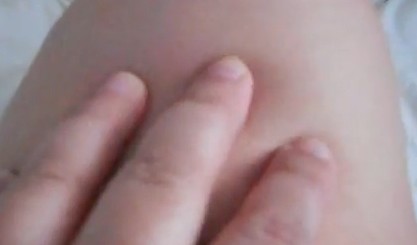
- When pressure is applied on the skin for several seconds, then it tends to retain a dimple at that spot.
- Pulmonary edema may cause symptoms such as pain in chest, breathing problems, and breathlessness. It is a severe condition that requires emergency medical care.
Causes of water retention
Water retention is caused due to leakage of fluids by the capillaries, i.e., the small blood vessels present across the body. The accumulation of such leaked fluid in the nearby tissues is what causes the characteristic swelling. Water retention can occur due to a variety of reasons. Some common causes are listed below.
- Water retention can occur due to intake of different medications like NSAIDS, hypertension drugs, estrogens, steroid medicines, and thiazolidinedione, a type of diabetic drug.
- People may experience mild instances of water retention due to:
- Increased consumption of salty cuisines
- Pregnancy. A woman may retain increased amounts of water and sodium during pregnancy to provide fluids needed by the placenta and the developing fetus. This can then result in water retention.
- Sitting or remaining is a specific posture for prolonged periods.
- As a part of symptoms that precede menstruation.
- Underlying diseases which can give rise to water retention include:
- Cirrhosis of the liver: Liver damage can cause water retention in the legs as well as in the abdomen.
- Congestive heart failure: The condition is marked by decreased or impaired ability of the lower chambers of the heart to effectively pump blood. This can trigger the accumulation of blood in the ankles, legs, and feet, resulting in edema. Cardiac failure can also cause the buildup of fluids in the lungs as well as abdominal swelling.
- Kidney damage: Any kind of injury or damage to the tiny blood vessels in the kidneys can adversely affect the process of filtering, thereby causing nephritic syndrome, a condition marked by reduced levels of albumin protein in the blood. This can then result in buildup of fluids in the body and subsequent water retention.
- Lymphatic system malfunction: Lymphatic system function includes removal of increased fluids from tissues. Any kind of damage to the system may hamper the draining activities of lymph vessels and lymph nodes in the affected area resulting in water retention.
- Kidney disease: It can cause malfunction of the organ leading to increased circulation of sodium and excess fluids in the body, thereby causing water retention. Affected individuals will usually exhibit swelling around the eyes and the lower limbs.
- Damage or weakness of the veins in the lower limbs: Persistent venous insufficiency is a condition marked by damage or weakening of the one-way valves present in the leg veins. Affected individuals will experience accumulation of blood in such veins resulting in swelling and water retention. A clot in the leg veins can cause sudden swelling in affected leg as well as mild to severe pain.
Remedies
It is very important to treat and get rid of water retention as untreated cases can cause varied health complications such as stiffness, walking problems, very painful swelling, scarring between tissue layers, high risk to developing skin ulcers and infections of the affected region, lowered blood circulation, discomforting, itchy, and stretched skin, and reduced elasticity of veins, arteries, muscles, and joints.
Following self-care techniques can help get rid of minor instances of water retention. Medications like diuretics can help treat severe water retention. In cases where water retention is caused due to intake of certain medications, the doctor will prescribe alternate medications. Treatment of underlying causative diseases can help alleviate illness-associated cases of water retention.
The below listed self-care measures can help find relief from the symptoms of water retention:
- Keep the affected part of the body in an elevated position above the heart’s level, many times in a day. You may also do so when sleeping.
- Protein helps remove excess fluids from tissues. A diet that is very low in calories can result in decreased protein content in the body. Eat a protein-rich and balanced diet to alleviate water retention.
- Exercising or moving the muscles in the region with water retention may facilitate the transfer of such fluids and decrease swelling.
- Use firm but not painful strokes to apply pressure on the affected areas. The strokes should be in the direction of the heart. This can help decrease water retention in that area.
- Ensure that the affected area is protected and well taken care of. Cracked and dry skin are at risk to cuts, bruising, and infection. Hence regularly moisturize the area and keep it clean to prevent infections. If the foot is swollen and has water retention, then adequate footwear as well as other protective measures are recommended.
- Decreased circulation of blood is one of the causes of water retention during pregnancy. Pregnant women should exercise as much as possible to facilitate blood circulation and avoid swelling of the legs, ankles, and feet.
- Doctors may recommend the use of compression sleeves, stockings, or gloves to compress the affected limb with water retention. The compression apparels will exert adequate pressure on the legs and arms and prevent the accumulation of fluids in the surrounding tissues.
- Salt tends to facilitate buildup of fluids and deteriorate an existing case of water retention. Hence, patients need to control the intake of salt in their daily diets.
- Yoga, meditation, and other methods that decrease stress can help prevent hormonal imbalances associated with PMS, thereby helping ease water retention.