Consumption of food that results in adverse reaction can lead to food poisoning. Food poisoning can therefore also be referred to as a ‘food borne condition.’ Food that contains contagious germs such as viruses, parasites, or toxins leads to unpleasant reactions after its intake. Some of the symptoms of food poisoning might be connected with gastrointestinal tract conditions causing vomiting, diarrhea, etc. It might also have an effect on other body parts such as the kidneys, muscle, or brain.
The most common symptoms of food poisoning are vomiting and diarrhea. Vomiting and diarrhea are not permanent and may last for about 48 hours; it often resolves on its own. But in some cases of food poisoning, a patient might suffer from dehydration, electrolyte abnormalities, and such other adverse symptoms which in turn affects the curing process. This can then cause food poisoning effects to persist for a longer time.
A CDC report states that approximately forty-eight million people become sick because of food poisoning. Also, along with that around three thousand fatal cases are reported. The report says that the main causes for food poisoning in United States of America are viruses and bacteria like clostridium, salmonellas, campylobacter, norovirus and perfringen.
Types of food poisoning
- Food poisoning occurs due to various reasons; these include bacteria, parasite, virus, and at times prions. There are more than two hundred contagious reasons for food poisoning. Microbes or germs could be in drinking water, swimming pools, rivers, lakes, infected food items, and also at day care centers.
- Listeria food poisoning can occur due to consumption of infected fruits, vegetables, raw milk, soft cheese, and meat. Elderly, newborn, expectant women, and people with weak immune systems are most susceptible to listeria food poisoning.
Causes, symptoms, and duration of food poisoning
Incubation period helps determine the cause for food poisoning. Incubation period can be classified as the time frame between consumption of the infected food and emergence of adverse reactions. There might be various causes for food poisoning. Some of the causes as per the incubation periods are given below.
1. Incubation period of about sixteen to twenty-four hours: Food poisoning marked by this short incubation period is caused due to:
- Chemical causes:It has a quick and fast start. It occurs because of the following reasons:
- Mushroom food poisoning could result in vomiting, diarrhea. Also, intake of ‘Amanita mushroom’ can cause liver and/or kidney to fail which can be fatal.
- Another form of chemical food poisoning is scombroid poisoning. It happens when stored or not fully cooked fish is consumed. In this, patient can experience adverse allergic reactions in one to two hours.
- Intake of toxins from fishes such as snapper, barracuda, and grouper, etc. causes ciguatera food poisoning. Symptoms such as vomiting, muscle pain, diarrhea, numbness, headache and hallucination may be experienced by the patient.
- Bacterial cause:Consumption of uncooked or not properly cooked rice causes bacillus cereus infection.
- When cooked meat is stored in extreme warm environment, clostridium perfringens spores attack such meat.
- Intake of such meat leads to severe diarrhea for about eight to twelve hours.
- Also, when food items with pre-formed toxins are consumed it causes staphylococcus aureus food poisoning. A person will vomit within one to six hours after intake of such infected food.
2. Intermediate incubation period between one to three days: These are:
- Large intestine infection:Colon or large intestine infection results in cramps and pain in abdomen as well as mucoid and/or bloody dysentery.
- In United States of America, infection by campylobacter is one of the major causes of food poisoning.
- Undercooked eggs or chicken or/and poor management while cooking can lead to salmonella food poisoning; this may happen in a day or more. Older people and those with not very strong immune system could suffer from this infection, which can be fatal.
- Food and water contaminated by Shigella spp might lead to bloody or mucoid diarrhea.
- Infected saltwater shellfish by vibrio parahaemolyticus can result in extreme diarrhea or watery loose stools.
- Small intestine infection: Small intestine infection causes irregular but concurrent large bowel infection and non-bloody dysentery. People who travel often usually suffer from E. coli food poisoning, but do not experience fever or bloody diarrhea.
- Viruses like adenovirus, rotavirus and Norwalk which causes food poisoning can result in many symptoms such as fever, headache, chills, and vomiting.
- Vibrio cholerae contaminated water, if consumed, can cause severe watery loose stools that may look like rice water.
- Botulism is caused due to consumption of food items infected by clostridium botulinum toxin. Some of its symptoms are fever, diarrhea, vomiting, numbness, and weakness, etc. It may also result in paralysis.
3. Long incubation period lasting for about three to five days: The reasons for food poisoning in this phase are:
- Hemorrhagic E. coli infection is one of the causes for food poisoning. Its symptoms are inflammation of intestine and bloody diarrhea. In this, bacterial toxin may pass into the bloodstream and destroy the red blood cells. This toxin could also lead to uremia, malfunction of kidneys, or kidney failure.
- For some kids there are chances of developing hemolytic uremic syndrome after a week of coming in contact with this infection, whereas older people may suffer from thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura.
- Food poisoning due to Yersinia enterocolitica infection can cause swelling of lymph nodes in the abdomen.
4. Lengthy incubation period of around 30 days:
- Parasites:Usually in tropical areas water is contaminated. If such impure water is consumed then it results in infectious amoebiasis food poisoning.
- Pork which is not properly cooked can cause trichinosis food poisoning. Some of its symptoms are fever, muscle pain, inflammation of face, gastrointestinal problems, and hemorrhage around eyes and below the fingernails.
- Water infected with pork tapeworm or tapeworm ova, if consumed can lead to cysticercosis food poisoning causing seizure and brain disease. Also, if food is not properly handled it may result in Hepatitis A viral infection.
- Intake of river/lake water which is infected by beaver, muskrat, or sheep can lead to infectious giardiasis food poisoning.
- Consumption of infected food/water can result in contagious cyclospora food poisoning. Its signs and symptoms are watery dysentery, headache, body pain, and malaise.
- Bacteria: Consumption of unpasteurized or unprocessed milk/cheese or goat milk infected by brucella spp. can cause brucellosis food poisoning.
- Consumption of contaminated beef by prions can lead to mad cow disease.
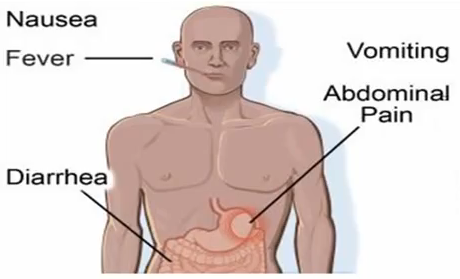
Treatment of food poisoning
Food poisoning can be treated as per the cause. Some of the treatment methods are as follows:
- To reduce pain, OTC pain killer medicines can be taken.
- Antibiotics can help in case of bacterial food poisoning.
- Lots of water and other liquids needs to be consumed for treating dehydration.