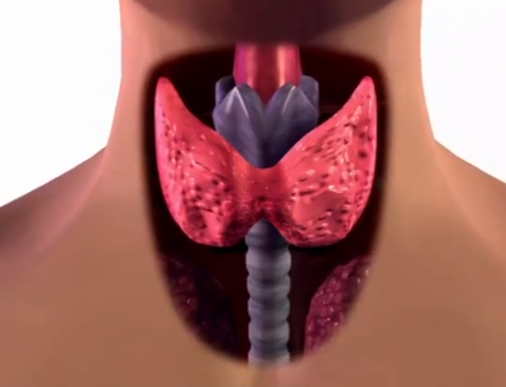
Graves disease is an autoimmune condition, which results in hyperthyroidism or overproduction of thyroid hormones. This condition is the most common cause for hyperthyroidism. Since Graves disease affects the synthesis of thyroid hormone, the symptoms are wide ranging. This disease can affect anyone but it is rarely life threatening. It commonly affects women before the age of 40. Since thyroid hormone affects many other body systems, this is why the symptoms are diverse. Treatment of Graves disease is aimed at inhibiting the production of thyroid hormone and lessening the severity of symptoms.
Causes of Graves disease
Graves disease occurs when there is dysfunction within the body’s immune system. Normally, the immune system responds to foreign substances by producing antibodies to target these substances. However, for a reason not well understood, the body’s immune system produces antibody to certain protein found on the surface of cells within the thyroid gland.
The function of thyroid gland is regulated by another tiny gland, which is located at the base of brain, and it is called the pituitary gland. The action of pituitary hormone can be mimicked by an antibody linked with Graves disease, the thyrotropin receptor antibody. This antibody can override the normal regulation of thyroid gland leading to overproduction of thyroid hormone.
When this antibody affects the function of thyroid gland, there is excessive production of thyroxine hormone. As a result, too much thyroxine leads to problems with the body metabolism activity, brain development, nervous and heart system function, muscle strength, body temperature, weight, menstrual cycles, and cholesterols in body.
Symptoms of Graves disease
Thyroid gland affects many systems of the body and the symptoms can vary widely depending on which systems are affected. The most common symptoms and signs are anxiety, irritability, fatigue, difficulties with sleep, and rapid heartbeat. A person with this condition may also experience fine tremor of hands and fingers. Increased perspiration and warm moist skin are also symptoms associated with the condition.
People may also have increased sensitivity to heat as well as weight loss in spite of normal eating. The thyroid gland becomes enlarged, a condition known as goiter. Women are likely to experience changes in their menstrual cycles while men may suffer from erectile dysfunction and reduced libido. Other symptoms include bulging eyes or Graves ophthalmopathy, diarrhea and frequent bowel movement.
A person with Graves disease may also suffer from Graves dermopathy where the skin becomes thick and red on top part of the feet or shin. Close to half of people with Graves disease suffer from an eye condition known as Graves ophthalmopathy. This eye condition causes inflammation and affects muscles and tissues around the eyes. Symptoms of Graves ophthalmopathy include bulging eyes, excess tearing, irritated dry eye, pain in eyes, puffy eyes, and sensitivity to light. It may also cause double vision, inflamed eyes, and gritty sensation in eyes.
Treatment of Graves disease
Inhibiting production of thyroid hormones and blocking the effects of the hormones in body are some of the treatment goals that are pursued to manage this condition. Radioactive iodine therapy is one treatment option applied. A patient takes radioiodine by mouth and since thyroid gland requires iodine to synthesis hormones; it takes up the radioactive iodine, which in turn destroys the overactive the cells of thyroid gland. This therapy causes shrinkage of thyroid and the symptoms of Graves disease lessen with time.
However, radioiodine therapy can increase the symptoms of Graves ophthalmopathy and therefore, it may not be recommended if a patient has moderate to severe eye complications. Radioiodine therapy may also have a temporary effect of increased thyroid hormone. This therapy is also not recommended in treatment of pregnant or nursing women.
Anti-thyroid drugs may be used to treat Graves disease symptoms. Such medications alter the function of thyroid in producing hormones. Some of the medications include methimazole and propylthiouracil. These drugs may be used before or after undergoing a radioiodine therapy to supplement the treatment of the condition.
However, these drugs can have side effects like joint pain, rash, liver failure and impaired function of the white blood cells that fight diseases. Methimazole can cause side effects in pregnant women such as birth defects and therefore, it is not recommended. Instead, propylthiouracil may be used for pregnant women.
Beta-blockers work by blocking the effect of hormones in your body. These drugs can provide relief of tremors, irregular or rapid heartbeats, irritability, and anxiety. They can also relief symptoms such as heat intolerance, diarrhea, sweating, and muscle weakness. Beta-blockers include atenolol, metoprolol, nadolol, and propranolol.
Since these beta-blockers can trigger asthma attacks, they are not prescribed to people with asthma. In addition, beta-blockers can complicate the management of diabetes and when they are abruptly discontinued, they can cause serious problems of the heart.
Surgery may be opted if the other therapies do not work effectively. If a patient suffers from Graves ophthalmopathy, other treatment options may be pursued such as use of corticosteroids to reduce swelling in eyes. Eye muscle surgery, prisms, and orbital therapy may be recommended to treat the Graves ophthalmopathy symptoms.
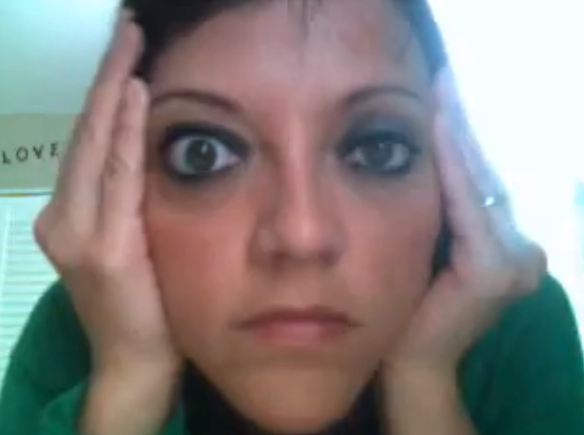
Graves Disease Pictures
Here are pictures of Graves Disease, notice how bulging eyes are a prominent feature of this medical condition.

Missy Elliott, the pop icon admitted to having Graves Disease
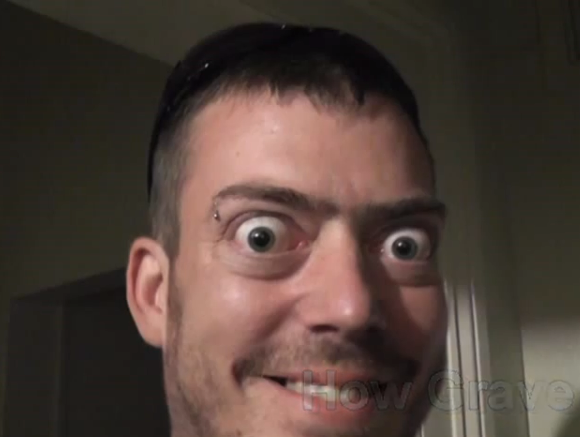




Former US President George Bush and his wife also have Graves Disease