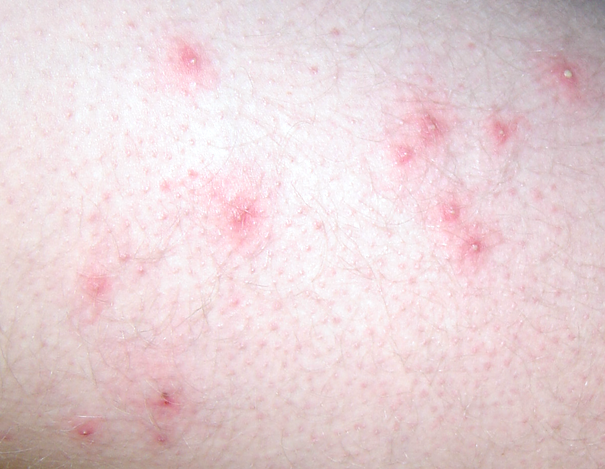
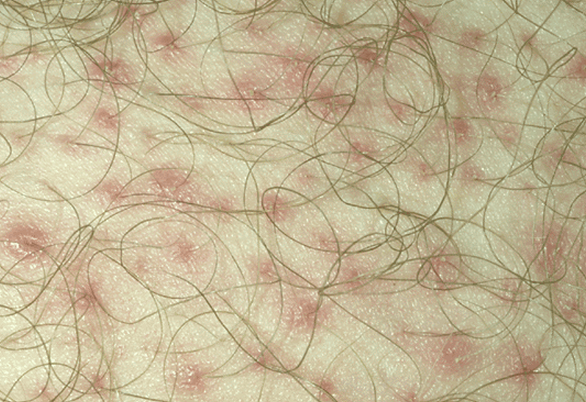
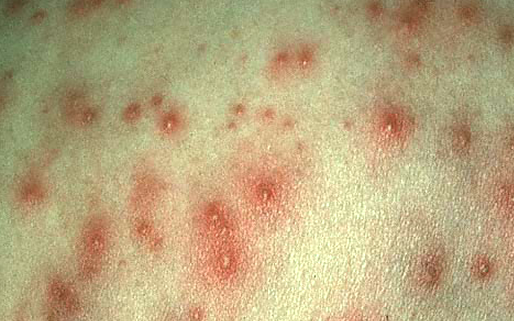
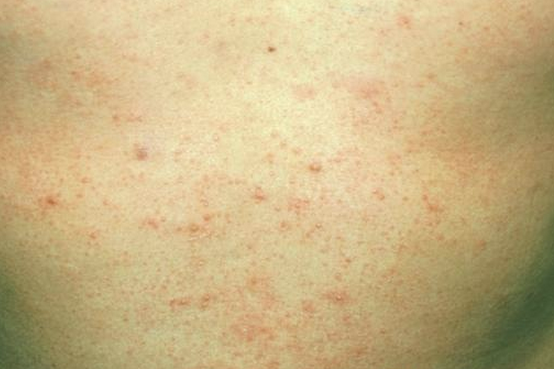
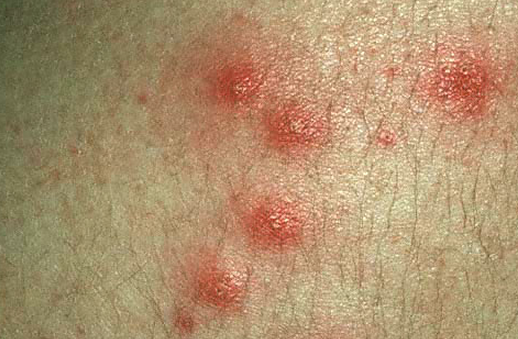
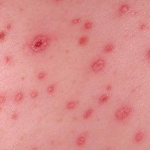
Folliculitis is a skin condition characterized by infection of the hair follicles by different bacteria, often by Staphylococcus aureus. Some types of folliculitis are also referred to as barber’s itch and hot tub folliculitis. Mild infections can be unsightly and discomforting, while serious infections can result in scarring and permanent loss of hair.
Hair follicles are the small pockets on skin from where hair grows. Folliculitis infections cause the formation of white-headed, tiny pimples near one or more hair follicles. A majority of folliculitis infections are shallow, itchy, and sometimes painful. Superficial folliculitis disappears on its own in some days. However, severe and recurring cases may require medical treatment.
Symptoms of folliculitis
The signs and symptoms of folliculitis may differ as per the kind of infection. Superficial folliculitis occurs in the upper portion of hair follicles and can result in the below listed symptoms:
- Tiny, pus-filled or reddish lumps may form in groups around the hair follicles.
- Skin inflammation and redness
- Pus-filled lesions may rupture, ooze pus, and then scab over
- Skin tenderness
- Itching
Deep folliculitis affects the complete hair follicle. It begins deep within the skin that surrounds affected hair follicles and cause below listed symptoms:
- A big, swollen, inflamed lump or mass
- Pain
- Pus-filled lesions may rupture, ooze pus, and then scab over
- In some cases, scarring may occur post healing
Types of folliculitis
The different types of superficial folliculitis are mentioned bellow:
Hot tub folliculitis or pseudomonas folliculitis
- It arises due to infection by pseudomonas bacteria which can flourish in varied environments such as hot tubs with badly regulated pH and chlorine levels.
- Circular, reddish, itchy, and bumpy rashes appear within 8 hours to 5 days after contact with the bacteria. Such rashes may later develop into pustules or pus-filled blisters.
- It is particularly worse in skin regions where contaminated water is held against it by the swimsuit.
Staphylococcal folliculitis
- Caused by staph infections, it is the most prevalent form of folliculitis. It can affect any part of the body that has hair follicles and is characterized by the formation of whitish, pus-filled, itchy bumps.
- It is known as barber’s itch when it occurs on a man’s beard region.
- The bacteria occur naturally on human skin and typically don’t cause health problems. However, their entry into the body via skin cuts, wounds, etc., can result in health anomalies.
Pityrosporum folliculitis
- This type of folliculitis is caused by a particular yeast and commonly affects adult men and teens.
- Symptoms include development of persistent, itchy, and reddish pustules on the chest and back, and occasionally on the shoulders, neck, face, and upper arms.
Pseudofolliculitis barbae
- It occurs when shaved hair in men curve back into the skin, and is characterized by inflammation of the beard-area hair follicles.
- Occasionally, men affected by this form of folliculitis may suffer from keloid scars.
The different types of deep folliculitis are listed below:
Sycosis barbae
- It affects men who have just started shaving.
- The entire hair follicle experiences inflammation. Tiny pustules initially occur on the upper lip, jaw, chin, and then become widespread with continual shaving.
- Extreme instances may lead to scarring
Boils and carbuncles
- These types of folliculitis are caused due to deep infection of the hair follicle by staph bacteria.
- Boils typically have a sudden onset with the development of a painful, reddish or pinkish bump, along with swelling and redness of surrounding skin. Later, it may fill with pus, grow bigger and more painful, and eventually burst and ooze. Tiny boils do not scar, while large boils may.
- Carbuncles are groups of boils that affect the shoulders, back of neck, thighs, or back. They are more severe than solitary boils. Hence, they form and heal over a period of time, thereby posing greater risk to scarring.
Gram-negative folliculitis
- It is caused by overgrowth of gram-negative bacteria due to alterations resulting from intake of antibiotics for a prolonged period.
- In most cases, the issue resolves after stopping the antibiotics dosage. In others, the harmful bacteria may spread and cause new, more intense acne lesions.
Eosinophilic folliculitis
- Its precise cause is not known, but it is more common in people with HIV.
- Recurrent clusters of pus-filled, inflamed sores affect the face, upper arms, and neck.
- The sores may itch severely, spread, and cause hyperpigmentation on healing.
Causes
Folliculitis is caused due to infection of damaged hair follicles by bacteria, fungi, or viruses.
Hair follicles can commonly get damaged via elevated sweating, friction from tight apparels or shaving, skin injuries, and inflammatory skin diseases, etc.
Folliculitis is usually not contagious. However, the infection can spread from one person to another via skin-to-skin contact, sharing of personal items like razors, etc., or via hot tubs and Jacuzzis.
Treatment of folliculitis
Mild cases of folliculitis resolve on their own. Severe cases may require medical treatment and the therapy is dependent on the type of folliculitis affecting a patient.
- Topical and oral antibiotics, antifungals, and corticosteroids are some of the medications used for treating varied folliculitis infections.
- Antihistamines and anti-itch creams may be given to alleviate itchiness
Folliculitis Pictures