A deer tick bite is one of the most misdiagnosed bites which resemble a mosquito bite. The deer tick is responsible for the spread of Lyme Disease as well as other diseases like babesiosis and human anaplasmosis. Bites from a deer tick causes bulls- eye rashes as well as headache, fever and fatigue. The symptoms may aggravate if left untreated and could even cause damage to the heart and brain.
A deer tick bite should be addressed to prevent more serious problems from occurring as early detection impedes various diseases from aggravating further. The doctor will prescribe the right medication to treat the specific disease that developed due to the tick bite. Still, bites from a deer tick can be prevented by taking precautionary measures when going into their dwelling places or handling tick-infested clothing or pets.
About the Deer Tick
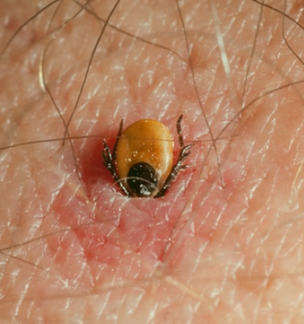
Deer ticks or Ixodes scapularis are a type of ticks that carry the bacteria that cause Lyme Disease. These ticks are as small as sesame seeds which puff out after feeding. They are found to be more active during May to July. Unlike other varieties of ticks, a deer tick has longer mouth parts which allow them to enjoy their blood meal up to 5 days. They choose large mammals as their source of nourishment and exhibit a preference for deer, which is the basis for its name.
A deer tick bite occurs when the parasite sucks on human blood for nourishment. The tick can attach to its human prey when the man brushes on deer tick-infested leaves, grass blades and animal’s coat. It will immediately settle in the moist places of the human body like the groin, armpits and knees and begin feeding. It should be noted that transmission of disease occurs after 24 hours, so if the tick is detected and removed early, the victim may not get the disease.
Appearance of a Deer Tick Bite
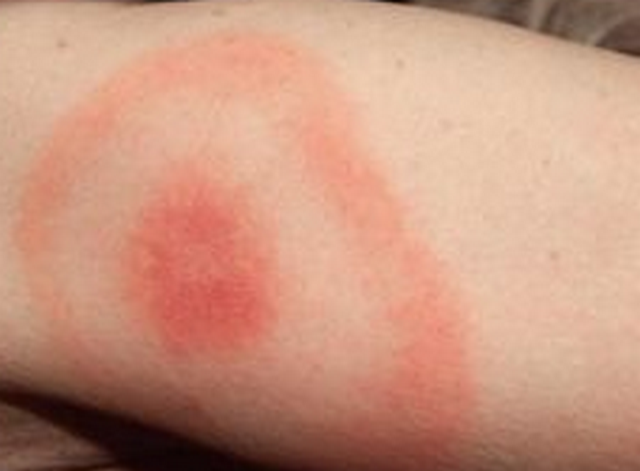
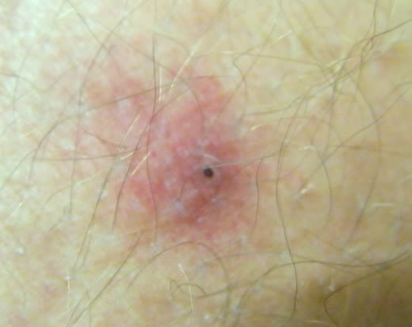
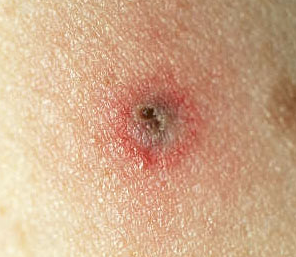
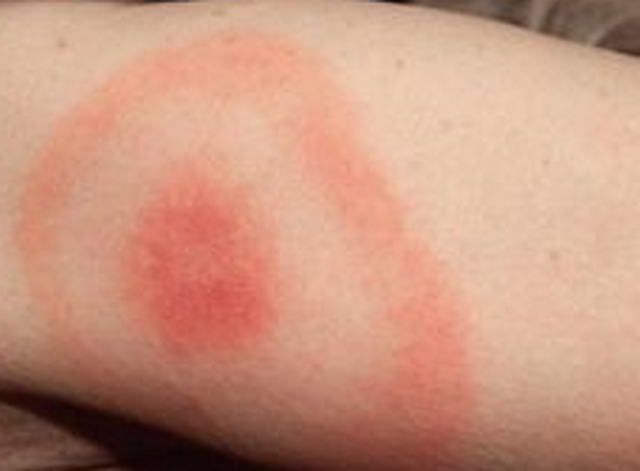
It is important to detect the bite of a deer tick the soonest time possible to lessen the likelihood of passing the Borrelia burgdorferi bacteria which causes Lyme Disease from the tick to human. The bite of deer tick is difficult to detect because it is painless and may look just like a mosquito bite. But once the parasite had finished feeding, the bite site will become reddish, swollen, itchy and have a burning sensation. The most distinguishing feature of a deer tick bite, which is a red and circular rash that is slightly elevated with a whitish center, then, develops. The rash will increasingly grow outward to form a bulls-eye.
The victim will eventually experience the symptoms of the disease several days to weeks after contracting the deer tick bite. Among these symptoms are:
- Headache
- Fever
- Sore throat
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Sore throat
- Inflamed lymph nodes
- Fatigue
- Arthritis
- Palpitations
- Breathing difficulties
A visible bulls-eye skin rash definitely helps in diagnosing Lyme Disease, but this does not appear in some cases which makes diagnosis tricky and even inaccurate. The victim should inform the doctor about having a tick bite and keep track of the symptoms. It would also help in the diagnosis of the disease if the offending tick is safely captured. To be able to arrive at a definitive diagnosis, the patient will have to go through a variety of tests.
Steps to take when bitten by a deer tick
First aid application on a deer tick bite employs the same approach for any insect bite. If the tick had already dropped off from the skin, the bite site should be washed with soap and water and treated with a disinfectant. If the tick is still attached to the skin, proper tick removal techniques must be done to prevent it from intensifying its efforts to release the contents of its guts thereby introducing the causative bacterium quickly. The proper way of removing deer tick involves the following:
- Use tweezers in removing the tick.
- Hold the tweezers close to the skin as much as possible as the head could be embedded into the skin.
- Pull the deer tick slowly. Make sure to get the entire insect.
- Drop the deer tick into a tightly-sealed jar or glass container and submerge in alcohol. It should not be squeezed to prevent the bacteria from spreading.
- Wash the bite site and apply disinfectant.
- Go to the doctor if the head is not removed or other signs and symptoms develop.
If the tick happens to reside on the hair, removal might be really difficult. The same technique also applies but make sure to clear away the hair to avoid getting caught up in the tweezers. Essential oils and other antibacterial agents help in faster recovery.
Preventing getting a deer tick bite
Prevention is the finest shield an individual could have to avoid getting a deer tick bite and contract Lyme disease. This could be done by:
- Avoiding shrubby and wooden areas.
- Avoiding tick-infested vegetation by walking in the middle of trails.
- Applying DEET-containing repellents when getting into tick-infested areas.
- Tucking long-sleeved shirt and pants to avoid ticks from getting into the body.
- Removing and checking the clothes for any ticks.
Deer tick bite pictures