Bullous pemphigoid refers to a skin disorder characterized by the formation of big fluid-filled blisters on those sections of the skin that tend to stretch frequently, like the muscles of the armpits, the lower abdomen, or upper thighs. It is a rare condition that is usually prevalent in the elderly over the age of 60 years.
Bullous pemphigoid is caused due to erroneous attack of the thin tissue layer occurring beneath the outer skin layer by the immune system. The exact cause of such anomalous immune system reaction is not known. However, the response can occasionally get triggered by intake of certain medicines.
Doctors generally prescribe corticosteroids and other immune system suppressing drugs to treat bullous pemphigoid. The skin condition can be deadly, particularly in those elderly individuals who are already suffering from failing health.
Symptoms of bullous pemphigoid
Some of the signs and symptoms of bullous pemphigoid are listed below:
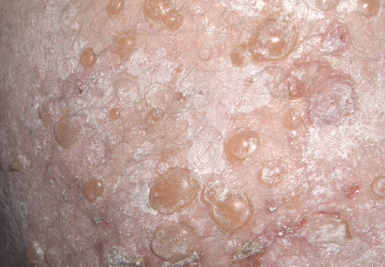
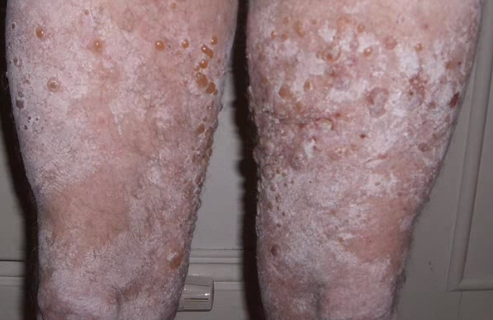
- Bullous pemphigoid can be easily identified by its main symptom, i.e., the occurrence of big blisters which are not prone to easy rupture. The blisters are filled with fluid that is generally clear but can sometimes consist of blood components. The skin surrounding the blisters may be reddened or of normal flesh color.
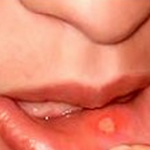
- Most patients experience the formation of bullous pemphigoid blisters on the groin, lower abdomen, arms, and upper thighs. The blisters are typically situated along the skin folds or creases, like those occurring at the inside portions of varied joints. Some affected individuals may also get affected by oral sores or blisters. In rare instances, the ocular mucous membranes can get affected, which in turn can result in soreness, redness, and discomfort in the eyes.
As bullous pemphigoid can be life-threatening, all cases of skin blisters that have no known causes like allergic reactions, etc., have to be checked by a doctor.
It is possible for the blisters to burst and create an open wound. Such wounds are at great risk to developing secondary infections. This can sometimes result in a deadly infection called sepsis that affects the complete body. This complication of bullous pemphigoid typically affects older patients with poor or failing health.
Bullous pemphigoid that affects the mucous membranes of the eyes or mouth can result in scarring.
Causes of bullous pemphigoid
The exact cause of bullous pemphigoid is still a subject of research and studies. It is however known that the condition is caused due to some dysfunction of the immune system.
Normally, the immune system of the body makes different antibodies to counter and fight off infections by bacteria, viruses, and other pathogens. In patients of bullous pemphigoid, the immune system however mistakenly produces an antibody for a specific skin tissue. The causes for this are not known.
The base membrane of the skin, i.e., the thin layer of fibers that connects the inner skin layer or the dermis to the outer skin layer called epidermis, gets adversely affected by the antibody associated with bullous pemphigoid. The antibodies result in inflammation of the skin which in turn lead to itchiness and formation of fluid-filled blisters.
There are no well-known risk factors that can trigger a case of bullous pemphigoid. It tends to occur at random. However, some studies have indicated that in rare cases bullous pemphigoid may be connected to some medical treatments as listed below:
- Radiation therapy for treatment of varied cancers as well as ultraviolet light therapy for treatment some skin disorders can trigger the onset of bullous pemphigoid.
- The skin condition can also appear due to intake of certain prescription medications such as etanercept, penicillin, furosemide, and sulfasalazine.
Bullous pemphigoid commonly tends to affect people who are more than sixty years old. The risk increases with an increase in age.
Treatment of bullous pemphigoid
Treatment of bullous pemphigoid involves the use of varied immune system suppressing prescription medications so as to completely heal the blisters and also ease the itchiness.
- Immunosuppressant drugs may be taken to suppress the adverse actions of the immune system.
- Doctors may prescribe oral corticosteroids, and/or topical corticosteroids to alleviate skin inflammation.
- Corticosteroid therapy may sometimes be combined with anti-inflammatory medications. Anti-inflammatories may also be prescribed as a standalone treatment option.
The below listed self-care guidelines can also help a patient find relief from the symptoms of bullous pemphigoid:
- Do not stay out in the sun for long durations. Cover the skin areas affected by bullous pemphigoid blisters when venturing out into the sun.
- The skin tends to become very delicate due to bullous pemphigoid as well as corticosteroid therapy. Hence, patients need to take extra care and avoid injuring the skin. Any rupture of the blisters needs to be checked by a doctor and then properly dressed to avoid secondary infections.
- Patients with oral blisters need to avoid crunchy and hard food items like raw vegetables and fruits, chips, etc. Consumption of these foods can worsen the symptoms.
Bullous Pemphigoid Pictures