Celiac disease refers to a digestive disorder which is activated by intake of the gluten protein. Gluten is mainly present in pasta, bread, cookies, pizza crust, and several other kinds of food stuffs that contain barley, wheat, or rye.Individuals with celiac disease elicit an adverse immune response in the small intestines after consumption of foods having gluten content. The reaction causes damage to the inner lining of the small intestine and results in an incapability to absorb some types of nutrients.
Celiac disease can lead to diarrhea and pain in the abdomen. Consequently, the lowered intake of nutrients which accompanies celiac disease can result in vitamin deficits which can rob the peripheral nervous system, liver, brain, bones, and other organs of essential nutrition.
There is no known cure for celiac disease. However, patients can efficiently control the condition by altering the diet.
Symptoms of celiac disease
There are no generalized signs and symptoms of celiac disease. A majority of patients experience usual symptoms such as:
- Sporadic diarrhea
- Bloating
- Pain in the abdomen
- In some cases, individuals with celiac disease may not experience any symptoms of the gastrointestinal system. It is also possible for the symptoms of celiac disease to be similar to signs of other disorders like gastric ulcers, irritable bowel syndrome, anemia, parasitic infections, and Crohn’s disease.
The reduced absorption of nutrients or malabsorption associated with celiac disease can be identified via the below listed symptoms:
- Loss of weight
- Bloating and gas
- Abdominal cramps
- Diarrhea
- Fatigue and overall weakness
- Stunted development or growth in children
- Grayish or bad-smelling stools which may be oily or fatty
- Osteoporosis
The less noticeable symptoms of celiac disease include:
- Depression or irritability
- Upset stomach
- Anemia
- Pain in the joints
- Skin rashes
- Muscle cramping
- Sores in the mouth
- Neuropathy or tingling sensations in the feet and legs
- Dental and bone conditions like osteoporosis
Untreated cases of celiac disease can result in many medical complications including neurological conditions, malnutrition, cancer, loss of bone density and calcium, and intolerance to lactose.
Causes of celiac disease
The exact cause of celiac disease is not known. Doctors are aware of the fact that certain reactions occur in people with celiac disease which causes the immune system of the body to adversely respond to intake of gluten foods.
The walls of the small intestine in healthy individuals contain villi, which are hair-like, tiny projections. The villi perform the function of absorbing minerals, vitamins, and other nutrition from the food that one consumes.Celiac disease causes destruction of the villi. The reduction in abundant villi results in inability of the body to absorb nutrients which are essential for growth and health. A lot of nutrients including proteins, fat, minerals, and vitamins are removed from the body along with the stool.
The causes of celiac disease may not be clear. However, doctors have found out that the disease tends to run in families. Hence, individuals who have family members with celiac disease are at a greater risk to developing the condition.Different studies have also found that certain types of gene mutations seem to elevate the susceptibility to celiac disease. However, the presence of such genetic mutations does not indicate that the affected person will definitely have celiac disease. This in turn signifies that there are many other factors which play a role in the development of celiac disease.
Some of the risk factors which increase the vulnerability to developing celiac disease are listed below:
- Autoimmune thyroid disease
- Type 1 diabetes
- Microscopic colitis
- Down syndrome
Treatment of celiac disease
There is no cure for celiac disease. However, patients can manage the condition by modifying the diet.
- People with celiac disease must avoid all kinds of foods which contain gluten, thereby preventing complications and managing the disease. Some of the foods that patients need to avoid are barley, wheat, rye, bulgur, farina, durum, graham flour, semolina, triticale, and spelt which is a kind of wheat.
- Patients can also consult a nutritionist to be able to get a gluten-free diet that is healthy and provides all the essential nutrients
- After the complete elimination of gluten from the diet, the inflammation of the small intestines will slowly diminish. It may occur after several weeks. However, patients will feel a whole lot better after only a few days.Redevelopment of the villi and total healing may occur after many months, even 2 to 3 years. It may be noted that intestinal healing occurs at a faster pace in children as compared to adults.
- The doctor may also suggest intake of mineral and vitamin supplements in cases of severe nutritional deficiencies. This will help fight malnutrition.
- Severe inflammation of the intestines can cause extreme abdominal pain. Such pain and inflammation can be alleviated with oral steroid medications.
- It is important to remember that even the lightest traces of gluten can adversely affect the small intestines in people with celiac disease. Patients may not experience any symptoms, but the intestinal damage will always occur. Hence, always avoid all gluten-containing foods.
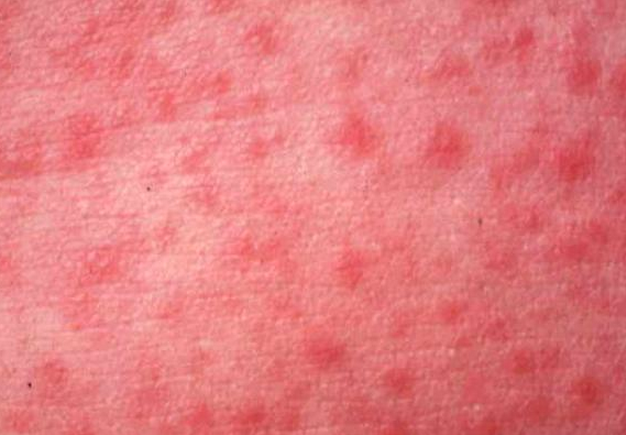
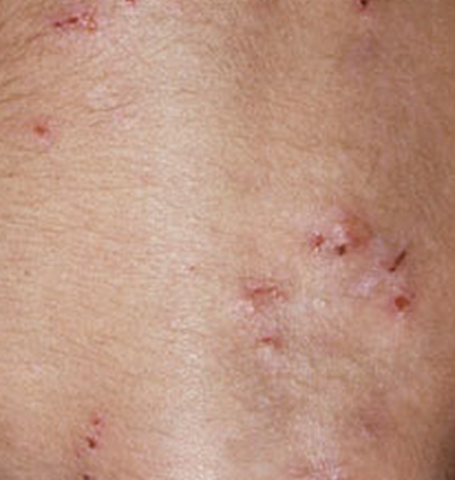
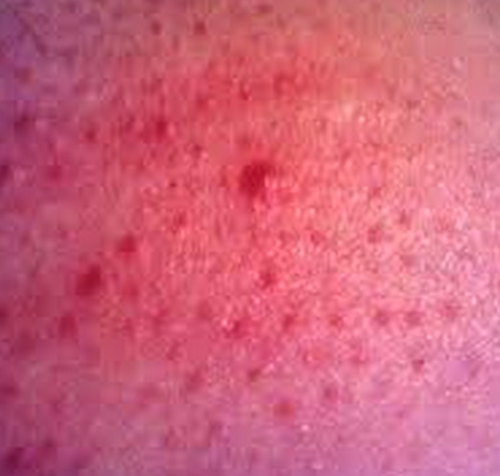
Celiac disease rash
Rash development is evident in some people with celiac disease. The type of rash that develops is also called dermal herpetiformis. It begins with a burning and itchy, red bumps around the knees, back, elbows, scalp and buttocks. The rash fades away with gluten-free diet and appropriate medication.
Celiac disease pictures