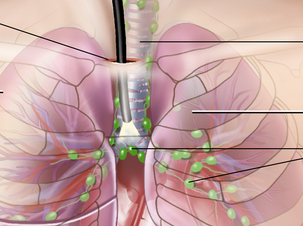
Lymph nodes are small glands that are bean shaped and are present throughout the body. They come under the lymphatic system that is responsible for carrying lymph fluids, essential nutrients, as well as the waste material from the body tissues to the bloodstream. This system is one of the most important parts of maintaining body’s immunity to strengthen the defense system in order to prevent disease. The filtering of lymph fluids is done through the lymph nodes flowing through them as it traps the foreign bodies, virus and bacteria that is later killed through lymphocytes or the also known as special white blood cells.
Lymph nodes are found collectively or singly and can be as tiny as a pin’s head or as big as an olive. Lymph nodes when collective can be felt in the underarms or near them, in the neck and around and in the groin. They can be found throughout the chest near the blood vessels and around the internal organs.
Symptoms
Symptoms of enlarged lymph nodes differ depending upon the causes. A person can actually be completely free of the signs but get diagnosed during a general medical checkup. At times the enlarged lymph nodes can be extremely sensitive and tender causing pain and disfiguration. Other symptoms could actually be significant of another underlying disease that could come with the lymph node enlargement.
Main symptoms of lymph node swelling are:
- Fever and nausea.
- Sweating at night.
- Loss in appetite.
- Weight loss.
- Local infections such as cold, sore throat, and even toothache.
Causes
Lymph nodes are usually not painful or tender and most of the enlarged lymph nodes especially when they are not in collective in the body cannot be felt. There is often swelling in one particular area if a problem like injury or infection, or tumor is present inside or around the lymph node. One of the main causes of enlarged lymph nodes is bacterial infection or illness such as tuberculosis. Even in cancer, especially in Leukemia and lung cancer, the lymph nodes get enlarged. Diseases such as Hodgkin and non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma are also another reason.
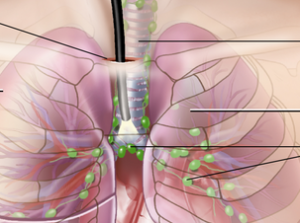
Diagnosis
Usually, tests like CT scans or Chest-ray are carried out in order to diagnose enlargement of the lymph nodes in the chest. A person might be ill with fever, cough or feel a lack of appetite and weight loss. There could also be a possibility of carrying out various blood tests in order to find out the most appropriate cause of the enlarged lymph nodes because many other diseases also lead to enlargement of the lymph nodes in the chest and the way of knowing what disease is responsible for the lymph nodes to be enlarged is tricky. That is why often the doctors need to perform biopsy for a better diagnosis to start with the right treatment.
If lymph nodes are present in an easily accessible area like the neck, armpits or groin the doctors often require a needle sample from these areas also called as fine needle aspiration cytology. The diagnosis also requires in some cases a huge piece of the lymph node or biopsy that could be performed in local or general anesthesia. However it completely depends on the area of the enlarged nodes. There are some patients who have enlarged lymph nodes in the chest but not anywhere else so with them the situation could be different but is doable with the help of CT scan. The sample however can be extremely small for the pathologists making it difficult to diagnose. It is also in some cases very dangerous to perform needle testing when the nodes are located very close to important organs and blood vessels. Earlier in such cases the patients went through open chest operation in order to get a lymph node sample. The new way however is a thoracoscopic biopsy of the lymph nodes that is done with general anesthesia. To look inside the chest the surgeon uses a telescope that has been connected to a miniature video camera with the help of a cannula. The telescope takes the picture of the internal chest and transfers it to the television screen. The sample is usually sent as soon as the procedure is finished to a pathologist for immediate processing also known as the frozen section. The complete diagnosis takes up to a week since the sample is supposed to be processed in a specific way and then there are a few special tests to be carried out further.
Why is a thoracoscopic lymph node biopsy better?
- Samples from the lymph nodes can be obtained adequately through a magnified view.
- More chances of removing single and smaller lymph nodes that could be difficult to obtain in biopsy under CT scan.
- Lesser pain as compared to surgery and the stay at hospital is shorter too.
- Takes less time for recovery.