Ebola is often a fatal disease of humans and other primates caused by ebola viruses. Ebola is undoubtedly the most deadly of all diseases, causing deaths of almost 25 to 90 percent of the patients with an average of more than 50 percent. Ebola can occur among humans as well as other primates such as gorillas and chimpanzees. The outbreak in West Africa in 2014 has been the largest ever in the history of public health. More than 70 percent of the patients have died. It was first discovered in the Democratic republic of Congo in 1976 near the Ebola River. Other countries that have been affected include Guinea, Liberia, Sierra Leone, Nigeria, United States, Spain, Senegal and Mali. However in October 2014, the World health organization had declared Senegal and Nigeria free of Ebola Virus emanation.
The signs start showing up from just two days to almost three weeks after the virus has been contracted. Symptoms include:
- Mild to high fever, cold and cramps.
- Sore throat, nausea, diarrhea, headaches, vomiting.
- Rashes and internal as well as external bleeding of the organs such as eyes, ears, nose, rectum.
- Low blood pressure due to fluid loss causing malfunctioning of the liver and kidneys.
The ebola virus spreads through direct contact by body fluids, for example the blood of the one who is infected, using any contaminated object, semen, breast milk, and saliva. These may also carry the virus for several weeks. The symptoms may also resemble to the ones of malaria, cholera, typhoid fever, meningitis and other viral hemorrhagic fevers.
How Ebola Spreads
It is communicable but not as easy as common flu, cold or fevers. Also, there is no scientific backing about the spread through air or water. It spreads through direct human contact in the form of body fluids but is not limited to that. The virus also penetrates through flesh cuts; break in the skin, through eyes, nose as well as mucous membranes. Bedding, Clothing, Needles and syringes and other Medical equipment are the most common carriers of the virus. However, it doesn’t spread through water, Air, food or Insects such as mosquitoes. Unfortunately, the health workers and others engaged in caring for the patients themselves are the most vulnerable as they have maximum chances of having a direct contact with the body fluids.
Ebola rash

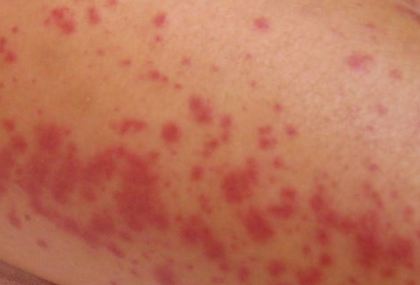
Ebola, like other severe diseases has side effects on the skin. Generally, in the first week of the illness the sufferer could experience mild rashes anywhere on the skin. The rashes are usually short lived and also are the sign of this disease. If the patient lives longer, then the rashes start peeling off looking like Sunburn. When the virus is present in a large amount then there might also be severe bleeding. Itching, redness, spotting are the common things to happen in such a rash. Later, it might also turn into Clots filled with abscess, following hemorrhaging that can affect internal organs such as liver, spleen, brain amongst many others. Usually after the rashes have been developed the hemorrhaging fever takes place. It destructs the same cells targeted in HIV AIDS, though more damaging it completely shatters body’s immunity.
If the skin condition persists for more than two weeks then it indicates the severe spreading of this infectious illness.
Treatment
Till now there has not been any specific treatment or vaccine for this virus but a large amount of research is being done at a huge scale. The recent outbreak had extensively coordinated medical care and services as well as community involvement from detection of the disease to treatment of those infected or the ones who came into the contact of infected individuals. Proper disposal of the dead was a special concern to prevent it from spreading further. Some other major preventive steps taken are as follows:
- Oral rehydration therapy i.e. a drink made of mildly sweet and mildly salty water.
- Fluids are usually given through the vein.
- Management of oxygen and blood pressure levels is also very crucial.
- Blood transfusions have to be made with the utmost care.
- Once survived, the person is immune for at least ten more years. But they must abstain from sexual intercourse for at least three months.
In order to prevent this fatal disease it is very important to have careful hygienic conditions. One must avoid contact with the infected person, especially through body fluids. Items used by the infected person must not be touched and hands must be kept clean all the time with the help of a sanitizer