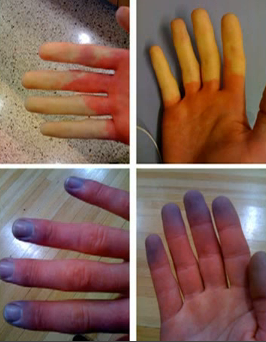
Raynaud’s syndrome is a condition wherein a person’s tips of fingers, toes, nose,and ears become numb and cold due to cold atmosphere or due to extreme stress.
Under circumstances of stress and coldness, people with Raynaud’s syndrome experience contraction of the smaller arteries which carry blood to the skin, thereby limiting the blood supply tothese areas and causing the classic symptoms
Raynaud’s syndrome is more common in women and in people living colder regions.
Symptoms of Raynaud’s syndrome
Individuals affected by Raynaud’s syndrome do not experience just cold fingers and feet. It is quite different from frostbite, and the symptoms are dependent on the severity, frequency,and duration of the sudden, involuntary, and abnormal contraction of the blood vessels. The following are the common symptoms of Raynaud’s syndrome:
Cold toes and fingers
In response to the stress and cold, the skin color of the affected partsinitially changesto white and then to blue along with a feeling of numbness and pricking. The sense touch is also repressed. When such areas are warmed or relived of stress, it results in stinging pain. The affected skin turns red, swells, tingles, and throbs when the blood circulation improves.
The syndrome may occasionally affect all or a few fingers or toes and the intensity may not be the same.It can also affect other body parts such as ears, nose, lips, nipples, etc. The duration of an attack may lastfor minutes or many hours.
Patients may also experience the symptoms of pre-existing disorders related to Raynaud’s syndrome.
Causes of Raynaud’s syndrome
- Patients of Raynaud’s syndrome suffer from contraction and over reaction of the blood vessels present in thefingers and toes when exposed to cold climates and/or stress. The exact reasons for such a reaction is not known.
- Patients experience thickening of artery walls on fingers and toes which dramatically reduces the blood supply to the skin in these areas, thereby causing it to turn pale and dusky. When the blood supply becomes normal, the affected area will redden before eventually becoming normal
- Raynaud’s syndrome may also be partially an inherited disability.
Types of Raynaud’s syndrome
- Primary Raynaud’s syndrome:It is the most common type of Raynaud’s syndrome and is not associated with any other underlying condition.
- Secondary Raynaud’s syndrome/Raynaud’s phenomenon:It is a serious but less common type of Raynaud’s syndrome. It is caused due to the presence of an underlying disease. It usually appears later in life, around the age of 40 years.
Causes of secondary Raynaud’s phenomenon
Following are some of the causes for secondary Raynaud’s phenomenon:
- Scleroderma: Majority of the persons affected by Scleroderma,a rare disorder causing scarring and thickening of skin, experience secondary Raynaud’s syndrome.
- Rheumatoid arthritis: Raynaud’s phenomenon may be the first sign of rheumatoid arthritis which is aninflammatory condition that causes joint stiffnessand pain.
- Lupus erythematosus: It is an autoimmune disorder which affects many areas of the body like joints, blood vessels, skin, etc.It common causes Raynaud’s phenomenon.
- Sjogren’s syndrome: Raynaud’s phenomenon may affect people with Sjogren’s syndrome, which is an autoimmune disorder that may follow lupus, rheumatoid arthritis, orscleroderma.
- Smoking: Smoking increases the risk as it narrows blood vessels.
- Artery disorders: Raynaud’s phenomenon may be associated with the following diseases of arteries:
- Buerger’s disease, aninflammatory disorder affecting the blood vessels of feet and hands.
- Primary pulmonary hypertension, a kind of high blood pressure affecting the arteries of lungs.
- Atherosclerosis is a disorder which slowly builds up plaques in blood vessels that supply blood to the heart.
- Injuries due to overuse: Repeated injuries on feet and handscan damage the underlying blood vessel nerves eventually causing secondary Raynaud’s syndrome. Old injuries also increase the risk.
- Certain drugs: Consumption of the following drugs can also cause Raynaud’s phenomenon:
- Some chemotherapy agents
- Beta blockers that are used to treat high blood pressure
- Migraine medications which contain ergotamine
- Non-prescription cold medications that narrow the blood vessels
- Estrogen containing medications
- Chemical exposures: Contact vinyl chloride can cause scleroderma, which can then cause Raynaud’s phenomenon
- Carpal tunnel syndrome: The carpal tunnel is a narrow tunnel-like tube in wrists that safeguard the major nerves of the hand. Carpal tunnel syndrome is a disorder that inflicts unusual pressure on the carpal tunnel nerves causing pain and numbnessof hand, thereby increasing the risk to Raynaud’s phenomenon.
Treatment of Raynaud’s syndrome
Depending on the cause of the syndrome, the medications are prescribed to widen the blood vessels for smooth flow of blood, and to control the symptoms. Following are some the treatment options for Raynaud’s syndrome:
- Alpha blockers such as prazosin and doxazosin are taken to control the actions of norepinephrine hormone that compresses blood vessels.
- Vasodilators such as losartan, sildenafil, fluoxetine, and prostaglandins are given for relaxing the vessels, and nitroglycerin is applied for healing the skin ulcers.
- Calcium channel blockers like nifedipine, amlodipine and feliodipine are prescribed for widening the blood vessels, to reduce the frequency and the severity of attacks, and to heal the ulcers of hand and feet.
- Beta blockers like metoprolol, nadolol and propranololare given for treating high blood pressure and heart diseases.
- Avoiding OTC cold drugs that contain pseudoephedrine.
- Avoiding birth control pills as it affects the blood circulation
- Chemical injections are given for blocking the sympathetic nerves in feet and hands.
- The gangrene affected fingers and toes where the blood supply is completely blockedmay require amputation.
- If necessary, nerve surgery may be performed tofree blood vessels from exaggerated response from the nerves.
Raynaud’s Syndrome Pictures