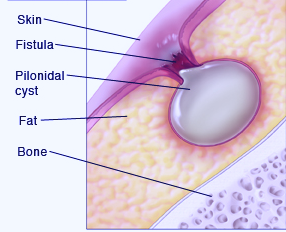
What is a pilondal cyst?
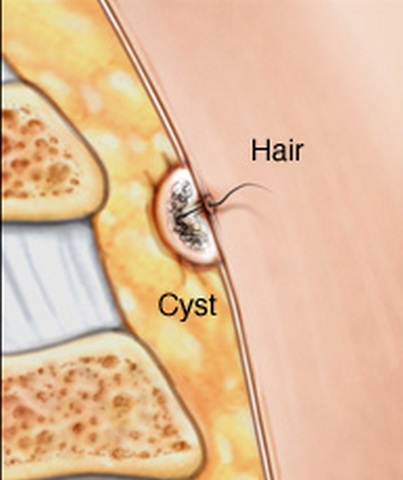
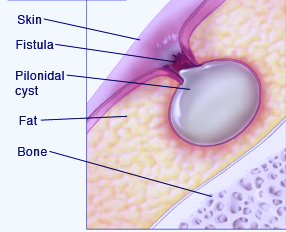
It refers to an anomalous growth in the skin which typically comprises of skin and hair debris. A majority of pilonidal cysts are often situated next to the tailbone, above the top portion of the buttocks cleft.
A pilonidal cyst usually develops when hair pierces the skin and then embeds itself into the skin. Infection of a pilonidal cyst can result in the formation of an abscess which is generally very painful. The cyst can be complete removed via surgery or it can be drained by making a tiny incision.
Young men are particularly vulnerable to the development of a pilonidal cyst. The abnormality also tends to recur. Individuals who have to keep sitting for prolonged periods, like truck drivers, are especially susceptible to developing a pilonidal cyst.
Symptoms
A pilonidal cyst turns into a swollen or inflamed mass, i.e. an abscess, when it gets infected. Some of the signs and symptoms of an infected pilonidal cyst are listed below:
- The affected skin may experience reddening
- Mild to severe pain, which can be sporadic or chronic
- Blood or pus may drain through an opening in the skin
- The drain pus may emit a foul odor
The presence of any kind of growth or lesion on the skin, especially near the tailbone region, requires medical attention. The doctor will examine the cyst and then offer an appropriate diagnosis and treatment option.
It is also important to note that chronic cases of infected pilonidal cysts, if left untreated, can increase the risk to developing a particular type of skin cancer known as squamous cell carcinoma.
Pilonidal cyst causes
The causes of pilonidal cyst is still a subject matter that is open to debate and interpretation. It is widely accepted that most cases of pilonidal cysts are typically caused by the penetration of loose hairs into the skin. Hairs can be pushed down into the skin via a number of activities that increase pressure and friction on the skin. A few examples include bicycle rides, excessively tight outfits, being in a seated position for prolonged periods, and rubbing of skin against skin. The body then identifies the hair as a foreign material and responds by creating a cyst around the embedded hair.
This theory can also be used to explain occasional cases of pilonidal cysts which develop on areas of the body other than adjoining the tailbone area. A few examples include the occurrence of pilonidal cysts in the skin present between the fingers, which can be observed amongst sheep shearers, pet groomers, and barbers.
There is another theory which propounds that the normal motion and extension of the deeper layers of skin can cause a hair follicle to enlarge and burst. It may be noted that a hair follicle is a structure which allows the growth of hair. The body then responds to a ruptured follicle by developing a cyst around it.
There are a number of risk factors which can increase the susceptibility to developing a pilonidal cyst. A few are listed below:
- A lethargic lifestyle
- Obesity or being overweight
- Excessive growth of hair
- Sports or jobs that require people to remain seated for lengthy periods of time
- Poor hygiene
- Rough or stiff hair
Treatment (surgery and other options)
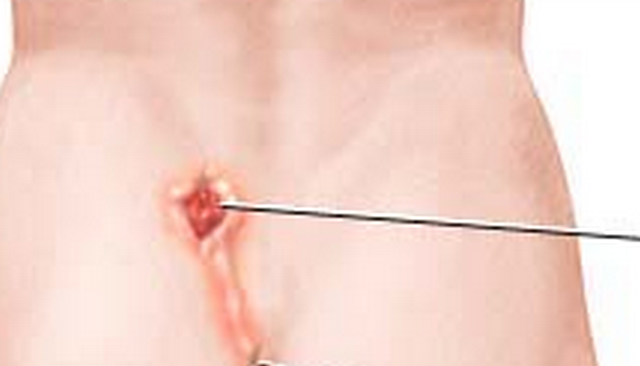
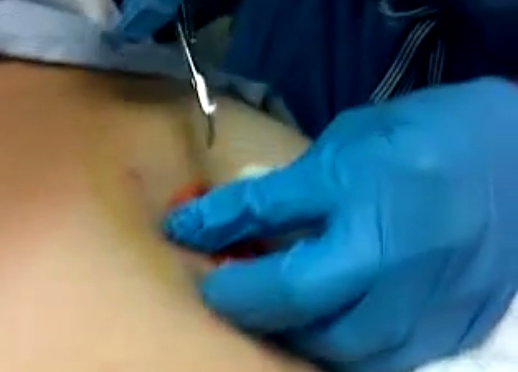
An infected pilonidal cyst which occurs for the first time is generally treated with a procedure that can be carried out in a clinic or a doctor’s office. The affected area is first numbed with an injection. The doctor will then make a tiny incision on the cyst to drain it. If the cyst develops again, which happens most of the times, patients may need to undergo a more protracted surgical procedure which will completely remove the pilonidal cyst.
The doctor may choose to do any of the below listed options after the surgery:
- Let the wound remain open: In this case, the wound caused by surgery is kept open and bandaged with dressing. This will allow the wound to heal from inside out. The healing time is longer when this process is used. However, it also results in lowered risk to a recurring case of pilonidal cyst.
- Stitch the wound shut: Closing the surgical wound with stitches may shorten the healing time, but it also increases the risk of recurrence. It may also be noted that some doctors make the cut towards the side of the buttocks cleft, where healing can be quite problematic.
Pilonidal cyst surgery recovery time
It is also important to take care of the wound post-surgery. The doctor or nurse will provide you with detailed instructions on when to come for a checkup, how to change the bandages, and how the process of healing will occur. The area around the surgical wound will also require regular shaving so as to prevent hairs from entering the surgical wound site. The recovery time which includes nursing and dressing up the wound can take about 60 days. Having diabetes or other medical issues can delay the healing process.
Pilonidal cyst pictures