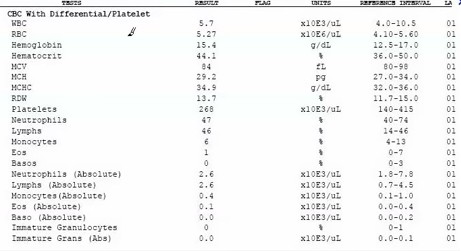
The CBC or the complete blood count test is a common and frequently requested type of diagnostic blood test. It helps determine and evaluate the cellular or developed constituents of blood. The examination and test work is typically performed on specific machines which have the capacity to ascertain the varied blood components in under a minute.
A large chunk of data produced by the CBC consist of values pertaining to the concentration of WBCs or white blood cells, RBCs or red blood cells, and platelets occurring in a sample of blood.
Complete Blood Count test: The procedure
- A complete blood count test can be carried out in varied settings such as a doctor’s office, clinics, labs, and hospitals, etc.
- In order to perform a CBC test, a few mm of blood is drawn out from the arm of a patient. The lab technician or a nurse will first cleanse a specific area of the arm, generally just near the elbow, with alcohol and then tap the area so that the vein can be seen. If the vein is not visible, then the nurse visualizes it; he/she then inserts a needle into the vein to collect the blood specimen. The needle is connected to a syringe, or a special vacuumed vial, where the blood is collected.
- The blood sample is then marked and sent to a lab for analysis and diagnosis of any diseases. For example, detection of low RBC count at the lab may indicate an underlying case of anemia.
Complete Blood Count test: Values of the different blood components
A complete blood count test will typically show the below listed values.
WBC count
- WBC count shows the number of white blood cells occurring in a specific volume of blood. The normal values of WBC count generally vary slightly from one lab to another; however the accepted normal value ranges between 4,300 and 10,800 cells, per cubic millimeter (cmm) of blood.
- WBC count can also be termed as the leucocyte count. In international units, it is stated as 4.3 to 10.8 x 109 cells per liter.
- The white blood cells differential count: White blood cells occur in varied shapes and sizes. The WBC count also shows the values of these different categories of WBCs. A white blood cells differential count will display the count of different WBC-cells like lymphocytes, monocytes, granulocytes, eosinophil, and basophils.
- There are 2 ways to determine the count of different kinds of white blood cells occurring in blood. One method is called manual WBC differential. In this, the blood sample is placed on a glass side and examined by a doctor or a trained lab technician under a microscope. The WBC types are manually counted. In the other method called automated WBC differential, the calculation of the percentage of different WBC types is done by a machine.
RBC count
- RBC count shows the number of red blood cells occurring in a specific volume of blood. The normal values of RBC count generally vary slightly from one lab to another; however the accepted normal value ranges between 4.2 and 5.9 million cells per cmm of blood.
- RBC count can also be termed as the erythrocyte count. In international units, it is stated as 4.2 to 5.9 x 1012 cells per liter.
- RBCs outnumber all other cells present in blood and are the most common. They are smaller in size than WBCs, but bigger than platelets.
RDW or Red Cell Distribution Width
- RDW refers to a calculated value of the variability in the size and shape of RBCs.
- The normal value ranges between 11 and 15. A higher RDW value means a larger deviation in size.
Platelet count
- Platelet count is the number of platelets present in a given volume of blood.
- The normal values of platelet count generally vary slightly from one lab to another; however the accepted normal value ranges between 150,000 and 400,000 per cmm of blood.
- In international units, it is stated as 150 to 400 x 109 per liter.
- Platelets are instrumental to the process of blood clotting/coagulation. Platelets are not complete whole cells. They are parts of cytoplasm belonging to a cell occurring in the megakaryocyte bone marrow. Cytoplasm is that part of a cell which is devoid of a nucleus or the body of a cell.
MPV or Mean Platelet Volume
- MPV is the value of the average size of platelet in a given volume of blood.
Hb or Hemoglobin
- Hemoglobin is a protein molecule present in RBCs. It supplies oxygen to the blood and imparts to it the red color. Hb is the value of hemoglobin levels occurring in a volume of blood.
- The normal range of Hb varies between men and women; in men it falls between 13 and 18 grams per deciliter, while in women it ranges between 12 and16.
- In international units it can be stated as 7.4 to 9.9 millimoles/liter for females and 8.1 to 11.2 for males.
Hct or Hematocrit
- It is the ratio of the volume of RBCs to the total volume of blood. Hematocrit values are typically ascertained via a process involving spinning down of the blood specimen in a test tube. As a result, RBCs collect at the foot of the test tube.
- The normal range of Hct value differs in men and women; it falls between 45% and 52% in males and between 37% and 48% in females.
MCV or Mean corpuscular volume
- MCV is a measured value that refers to the average volume of a red blood cell. It is calculated from Hct and RBC count.
- The normal range falls between 80 and 100 femtoliters. Femtoliter is a miniscule proportion of 1/millionth of a liter.
MCH or Mean Corpuscular Hemoglobin
- MCH is a measured value that refers to the average amount of hemoglobin in an average red blood cell. It is calculated from Hb and RBC count.
- The normal MCH values range between 27 and 32 picograms.
MCHC or Mean Corpuscular Hemoglobin Concentration
- MCHC is a measured volume that refers to the average concentration of hemoglobin in a specific volume of red blood cells. It is calculated from Hct and Hb count.
- The normal MCHC values range between 32% and 36%.