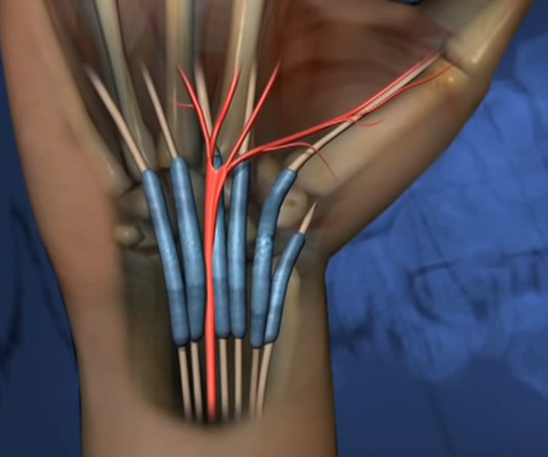
Carpal tunnel syndrome is an anomaly of the tight area present between the arm-joints that hold up the wrist bone and fibrous tissues.
The carpal tunnel is a thin passage, supported by ligaments and bone, and situated wrist’s palm side. It helps protect the nerves of the hand and 9 ligaments that manage the movement of fingers. When these particular set of nerves get compressed then it results in tingling, numbing sensations, and pain in the fingers and palm, and the resultant condition is referred to as carpal tunnel syndrome.
The median nerve that goes through the carpal tunnel gets sensation from different fingers like the thumb, index finger, middle finger and ring finger. When this center nerve gets irritated and squeezed, due to varied causes,then it results in carpal tunnel syndrome. Patients experience tingling and numbness in the index, middle, and ring fingers, as well as the thumb. Several factorscan cause carpal tunnel syndrome, including presence of some disease, anatomy of wrist, pattern of hand, etc.
Correct timely treatments bring comfort, alleviate the symptoms, and heal the condition. Untreated instances may however slowly spread to the hand and forearm.
Symptoms of carpal tunnel syndrome
Some of the symptoms of carpal tunnel syndrome are as follows:
- Tingling feelings and numb sensationsare felt in all the fingers apart from the little finger. Similar sensationsmay also affect the hand.
- It is important to remember that if the syndrome is left untreated then the numb and tingling sensations can become regular.
- Loss of strength in arms and decreased or absent ability to hold things
- Weakness in hand
- Pain can radiate from wrist to hand, upper arm to shoulder, and later to palm.
Causes of carpal tunnel syndrome
Carpal tunnel syndrome forms as a result of excessive tightness or compression of the median nerve in the wrist.
There may be only one or many factors that may enhance the risk for development of this disorder. These risk factors are as follows:
- Working condition: If an individual has to do work with vibrating tools or a kind of work which requires twisting of wrist repeatedly, then such work may damage the median nerve.
- Inflammatory condition: Such conditions can arise due to diseases like rheumatoid arthritis, infectionsaffecting the wrist tendons, etc., which can then put additional pressure on the median nerve.
- Alterations in the balance of bodily fluids: The normal balance of body fluids can get changed by some conditions like obesity, kidney failure, menopause, thyroid disorder, pregnancy, etc. This leads to excess pressure on the carpal tunnel. However, if the carpal tunnel disorder is caused because of pregnancy then it disappears on its own after the baby is born
- Conditions that result in damage to the nerve: Severe chronic diseases like diabetes and excess and daily intake of alcohol increase the risk of carpal tunnel syndrome because it may damage varied nerves such as the median nerve.
- Anatomy of the wrist: Unexpected and unusual pressure can be created in the nerve due to a facture in wrist or its dislocation. This can change or tighten the space in carpal tunnel leading to carpal tunnel syndrome.
- Gender: Usually, females are at greater risk to developing this disorder as they have a narrower carpal tunnel in comparison to males.
Diagnosis
The below listed diagnostic tests help in determining an underlying case of carpal tunnel syndrome:
- Physical examination: Physical examination of palm muscles, fingers, wrist, and nerves; all these help to ascertain and recognize the symptoms of carpal tunnel syndrome.
- Pattern of signs and symptom: If a person loses sensation in the little finger then it indicates the presence of some other disorder because in carpal tunnel syndrome the little finger is not affected. One more way to diagnose the syndrome is the timing of the signs and symptoms of this disorder. For example, if an individual faces problem in holding a steering wheel, phone, reading a book etc., then these signs may point to presence of this syndrome.
- X-ray: X-rays of wrist help to know the cause of the disorder; whether it is due to arthritis, fracture, etc.
- Electromyogram: In an electromyography a thin needle electrode is inserted into the muscles, when resting and while doing activities. The electrical activities of the muscles are then examined to confirm any harm done to the muscles.
- Nerve conduction study: In such studies, 2 electrodes are placed above the skin and thenmild shock is passed on the median nerve to know the deceleration of electrical impulses in carpal tunnel. This further indicates the presence of carpal tunnel syndrome.
The above two procedures, namely, electromyogram and nerve conduction examinations also assist in identifying the probable disorders that elicit signs parallel to those experienced with carpal tunnel syndrome.
Treatment of carpal tunnel syndrome
Some of the treatment options for carpal tunnel syndrome are discussed below.
Reduction of sporadic inflammation: An affected individual can apply cold packs and give rest to hands. If this still doesn’t lessen the swelling then some extra treatment methods are wrist splinting, medications, and surgeries. Treatment like wrist splinting can assist only in cases of mild to moderate symptoms that tend to persist for a period of not more than ten months.
Nonsurgical therapies can also assist to alleviate the symptoms of the conditions. They include:
- Intake of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medicines: It helps to improve the adverse symptoms and is a good treatment option for relief over a short period.
- Wrist splinting: It assists in controlling tingling sensations and numbness. In case of pregnant females nocturnal splinting is a better option.
- Corticosteroids use: Corticosteroids helps to control inflammation, pain, swelling, etc., and lessens the pressure on the median nerve. Also it is assumed that if corticosteroids are injected they are more effective for this disorder.
Surgeries: In case the above nonsurgical therapies do not work and/or reduce the pressure on the median nerve, then open or endoscopic surgery may be suggested by doctors.
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Pictures